
American progressives long have looked upon Britain’s Labour Party as an exemplar of how to prioritize social welfare without entirely alienating business. Unlike their European counterparts, whose overly suspicious view of wealth and overly generous view of social welfare spending make poor role models for America, the British Labour Party has brokered a “partnership” between wealth and welfare over the years more suitable to the American psyche.
Yet today that partnership is nearing collapse. For over a decade Britain’s supercharged financial sector fuelled the growth of an expansive state. But as the financial sector has cooled, Britain’s Labour party is now faced with the stark reality of burgeoning social welfare commitments, unprecedented public debt, and dubious upward mobility prospects for the ordinary citizen. The government has seemed more competent at creating upward mobility for civil servants who service the growing social welfare state than doing the same for the larger population who have to pay for it.
Now the question for Labour – and the UK – is how to maintain an expansive social insurance program by somehow creating the kind of growth needed to pay for it. Once its “wealth creation strategy” of relying on a fecund banking sector fell apart, its project of providing income security rather than fostering income growth for ordinary people appears to be on the verge of failure.
In order to maintain social welfare goals amidst a floundering economy, the UK has financed its shortfall through massive debt – something the average British household knows something about. Between 1997 and 2007 average household debt grew from 105 to 177 percent of disposable income. The US, of course, also experienced an explosion of household debt during the same period but not nearly to the same extent. At the end of 2007 America’s average household debt reached 106 percent of disposable income – essentially where the UK started 10 years earlier.
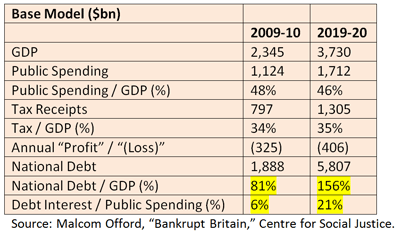
The UK’s comfort with personal debt has now extended to the public realm. Even before the recession, Britain had $1.2 trillion of public debt, and by next year it will rise to $1.8 trillion, or 81 percent of GDP. If debt payment were a government agency, it would be the fourth largest in Britain. According to the London-based think tank the Centre for Social Justice, 21 percent of total public spending will be devoted to debt service in 2020, compared to 6 percent today. Public debt in the US, by comparison, will reach 60 percent of GDP by next year, and interest on the debt will rise from 4.6 percent to nearly 14 percent ten years from now. Labour’s legacy will be the Mount Everest of indebtedness it has left the current and subsequent generation.
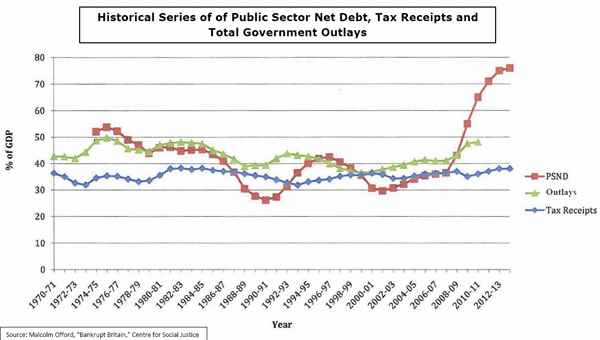
To put this in perspective, we need look no further than historic trends over the past 30 years. Public debt has tracked fairly proportionately with public spending in the UK during this period. During the economic stagnation of the late 1970s, public debt rose to nearly 50 percent of GDP. It hit its nadir at around 25 percent in 1990 after the Thatcher era, and then rose to around 35 percent, where it has remained ever since – until last year. Suddenly, debt has skyrocketed to more than 75 percent of GDP in the past year – an unprecedented level – and will rise to 100 percent by 2012 before swelling to 150 percent by 2020. In order to reduce debt to its 45 percent level of just a few years ago, public spending would need to be cut by a third. Given that one-fifth of all public spending will go to debt service in 10 years, cutting spending will prove politically impossible for a government – and perhaps an entire nation – that identifies ever expanding government-funded services as essential.
Even more disquieting, tax receipts have mainly hovered around 35 percent of GDP regardless of the tax rate during the past 30 years. This means that raising tax rates – such as Labour’s proposal to lift the top tax bracket to 50 percent– have little effect as high earners move away or find other ways to protect their assets. Logically, if it hopes to cope with its debt obligations, Britain should therefore keep taxes as low as possible and cut public spending. But instead the UK drives full-speed ahead into the fog of debt without having any notion of how to service its future obligations.
The UK is therefore faced with a thorny dilemma: on the one hand, it has spent decades creating a social welfare system that reduces risk and promises citizens protection from life’s vagaries, and on the other, it needs people to take risks in order to revitalize the economy. Government spending fostered risk avoidance precisely when Britain most needs an entrepreneurial class that can help diversify the economy away from finance and, to a lesser extent, tourism.
The people most hurt by social welfare are young working class people – the very group Labour purports to represent. In the UK there’s much talk about the NEETs – young people in their late teens who are Not in Employment, Education, or Training. In 2000 there were 630,000 young people between the ages of 16 and 19 in this group. Today, that number totals 860,000, a 36 percent increase in less than a decade. This would be the equivalent of 4.5 million young people in the United States. If NEETs were a city, they would be the third largest metropolitan area in the UK.
Increasing numbers of able-bodied young people dropping out of society altogether reflects a growing sense of hopelessness. According to the Gallup World Poll, only 20 percent of 25-34 year olds, and 25 percent of 35-49 year olds, thought the economic conditions in the UK were good before the current economic crisis. The UK’s NEET problem and economic pessimism were rampant when the going was good – something that can only be worse now.
This is not merely the result of a profligate welfare state. The NEET problem has its origins in complex cultural phenomena. However, it is difficult to argue with the conclusion that an increasing economic resignation among Britain’s younger population is ill-timed for a government betting on future workers to pay the public mortgage.
The US has a more diversified economy than the UK and likely suffers from less economic resignation, but it is beset with a similar dilemma. Despite historically unprecedented levels of public debt, albeit less extreme than Britain’s, the Obama administration appears to be pursuing an economic program that bears similarities to the Labour preoccupation with creating prophylactics against risk and hardship. In a matter of months, the US deficit has risen from 3.2 to 13.1 percent of GDP, according to the Congressional Budget Office.
Even with President Obama’s widely doubted promises to cut the deficit in half, the CBO estimates a yearly shortfall of more than $1 trillion ten years from now. Even worse, there is precious little in the administration’s plans – including its grandiose claims about “green jobs” – that will create the growth necessary to carry such debt in the future. In fact many of the administration’s proposals – from its healthcare program to its auto company ownership and a more heavily regulated financial sector – could serve more to curb growth than encourage it. In addition, increased taxes on “the rich” will hit small businesses most grievously, the most plausible engine for growth.
It appears the administration seems intent on following Labour’s folly of mortgaging the future. Without addressing the issue of how to unleash the entrepreneurial energies of the young generation, it’s hard to see how America will avoid falling into the morass in which its British cousins are now so perilously trapped.
Ryan Streeter is Senior Fellow at the London-based Legatum Institute.












