NewGeography.com blogs
For years, the world's busiest airports in passenger volume have been Atlanta's Hartfield-Jackson International and Chicago's O'Hare. However, there are indications that this long dominance may be about to end. According to Airport Council International data for 2009, Chicago O'Hare had fallen to 4th position, following Atlanta, London-Heathrow and Beijing Capital International Airport.
Beijing's Capital International increased its passenger volume by 17% in 2009, while European and American airports were experiencing slight declines due to the recession. Beijing's increase is more significant, because growth might have been expected to level off after the 2008 Olympics, which were held in Beijing. Between 2008 and 2009, Beijing rose from 8th in the world to 3rd, and from 20th place in 2004, when its volumes were approximately one-half the present level.
Early 2010 data (first quarter) indicates that Beijing Capital International has become the second busiest airport in the world, trailing only Atlanta. Passenger volumes were up 10.5% from a year earlier. If the current rate of growth continues, Beijing should pass Atlanta in two to three years, even if the American economy improves.
London's 130 million annual passenger traffic was the greatest of any metropolitan area in the world in 2009 (distributed among five airports). The new Conservative-Liberal Democrat government seems determined, however, to forfeit this ranking, having banned further London airport expansions to combat what it calls "binge flying."
New York was second with passenger traffic of 105 million at its three major airports, while Tokyo was third at 95 million. "Binge flying" does not seem to be a concern in Japan, where Tokyo's Haneda Airport is adding a fourth runway and will soon serve international flights again, providing competition to more distant Narita. Atlanta's single airport handles an annual passenger volume of 88 million.
Other airports in China are also growing. In the Pearl River Delta (the world's largest "mega-region," an area of adjacent urban areas), the four large airports, Hong Kong, Guangzhou and Shenzhen accommodated passenger traffic of more than 105 million in 2009. Traffic at Shanghai's Pudong and Hongqiao grew 14% and 10% respectively.
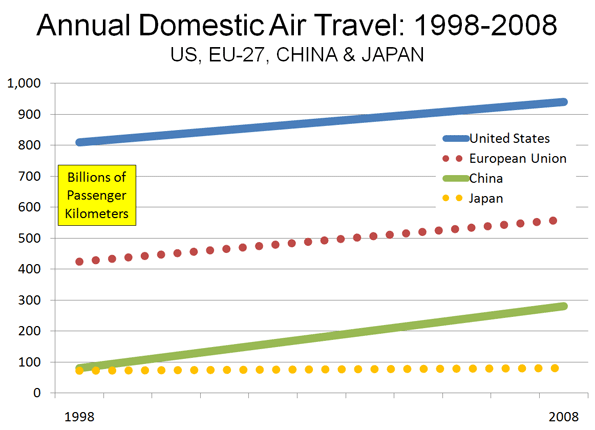
Overall Chinese air traffic is also growing rapidly. Over the past 10 years, annual passenger volumes have risen an average of more than 25%. This compares to an average annual growth rate of 3.2% in the European Union (EU-27), 1.6% in the United States and 1.1% in Japan (Figure). The US continues to be dominant in passenger volumes, at 940 billion annual passenger kilometers, compared to 560 billion in the European Union, 280 billion in China and 80 billion in Japan (data calculated from US, Europe, China and Japan national sources).
If Tara Siegel Bernard of The New York Times is right, (city of) New Yorkers must be among the most irrational people in the world. In "High-Rise or House with Yard," she describes the purported financial advantages of living in a co-op apartment in Brooklyn versus suburban South Orange, New Jersey.
The irrationality is that, despite the money that households can save by staying in the city, a net more than 350,000 left for the suburbs between 2000 and 2007, as E. J. McMahon and I found in Empire State Exodus, which summarized IRS inter-county migration data. Indeed, each of the city's five boroughs lost domestic migrants to the suburbs during the period. An analysis by The New York Times itself found that the city had lost net domestic migrants to every suburban county in the metropolitan area as well as to every county in newly exurban northeastern Pennsylvania. This includes Allentown-Bethlehem and Scranton-Wilkes Barre, toward which New Jersey land use regulations have driven new development.
 "High Rise or House with Yard" stands alone in claiming that New York City is less costly than its suburbs. The most recent (and authoritative) ACCRA cost of living index for Brooklyn is a full 40% higher than in the South Orange (the Newark-Elizabeth area). This is before considering the fact that the Brooklyn home is a 1,000 square foot coop apartment with two bedrooms and one bath, while the suburban home is a 2,000 square foot house in South Orange with four bedrooms and 2.5 baths. Smaller apples may well be less expensive than bigger oranges. The Times also assumes that the suburban resident will commute by train to Manhattan, at more than $400 per month. It is also possible that, like 80% of South Orange commuters, the new suburbanite may choose to work in the New Jersey suburbs. Maybe New Yorkers are not all that irrational after all. "High Rise or House with Yard" stands alone in claiming that New York City is less costly than its suburbs. The most recent (and authoritative) ACCRA cost of living index for Brooklyn is a full 40% higher than in the South Orange (the Newark-Elizabeth area). This is before considering the fact that the Brooklyn home is a 1,000 square foot coop apartment with two bedrooms and one bath, while the suburban home is a 2,000 square foot house in South Orange with four bedrooms and 2.5 baths. Smaller apples may well be less expensive than bigger oranges. The Times also assumes that the suburban resident will commute by train to Manhattan, at more than $400 per month. It is also possible that, like 80% of South Orange commuters, the new suburbanite may choose to work in the New Jersey suburbs. Maybe New Yorkers are not all that irrational after all.
Moreover, people are moving even further than the suburbs and exurbs, with almost as many people moving from New York City even further away. The latest Bureau of the Census data indicates that every borough experienced a net domestic migration loss between 2000 and 2009. More than 1.2 million residents left New York City, nearly as many people as live in the cities of Washington and Boston combined.
- Manhattan lost more than a 140,000 net domestic migrants, more people than live in the city of Hartford.
- Brooklyn lost nearly 450,000 net domestic migrants, more people than live in the city of Miami.
- Queens lost a 420,000 net domestic migrants, nearly as many people as live in the city of Cleveland.
- The Bronx more than 200,000 net domestic migrants, more people than live in the city of Providence, Rhode Island.
- Staten Island did much better, losing only 5,000 net domestic migrants. But then, much of Staten Island looks more like suburban New Jersey than New York City
In the face of these losses of which at least some at The New York Times are aware, the article notes that "Many empty-nesters are giving up the high-maintenance house in the suburbs in exchange for the attractions of city life." Not that many.
Photo: New Jersey Suburbs
Even though cities all over the United States are running large deficits, Chicago Mayor Richard Daley feels that an investment in one particular charity is an investment for the future. After School Matters, founded by Mayor Daley’s wife Maggie Daley, funds l youth programs and helps low-income youth obtain job skills. It has received more than $46 million from the city since 2005, with nearly one-third of that total coming in 2009 alone ($15 million). This is a 50% increase from 2008, when the charity received $9.36 million.
The city has even given some of its federal stimulus package to fund After School Matter’s job program, which pays low-income 14 to 24 year-olds $9-$10 an hour for four and a half hours of work each workday. The contract, signed in 2009, has allotted $1.31 million to the charity for three years. However, Illinois lags behind its projected job growth, and Mayor Daley must find a way to create sustainable jobs for these new workers if he is going to justify this allotment of stimulus money.
Aside from that, companies that have contracts with the city are donating money to the project as well. Mayor Daley may not be accepting money from city contractors for his campaign, it certainly does not hurt that these contractors are giving millions to his wife’s charity. The Mayor has encountered a lot of criticism for patronage in City Hall after his nephew was found to have used city pension money to buy union land. After School Matters may represent a much more righteous investment, but the Mayor’s seems determined to make Chicago’s budget a family affair.
Hat tip to Steve Bartin’s Newsalert
IBM has released its annual "Commuter Pain Index," which ranks traffic congestion in 20 metropolitan areas around the world. According to IBM, the Commuter Pain Index includes 10 issues: "1) commuting time, 2) time stuck in traffic, agreement that: 3) price of gas is already too high, 4) traffic has gotten worse, 5) start-stop traffic is a problem, 6) driving causes stress, 7) driving causes anger, 8) traffic affects work, 9) traffic so bad driving stopped, and 10) decided not to make trip due to traffic."
Each metropolitan area is given a score between 0 and 100, with the highest score indicating the worst traffic congestion (See Table).
| IBM Commuter Pain Index: 2010 |
| Metropolitan Areas Ranked by Worst Traffic Congestion |
|
|
|
| Rank |
Metropolitan Area |
Score (Worst to Best) |
| 1 |
Beijing |
99 |
| 1 |
Mexico City |
99 |
| 3 |
Johannesburg |
97 |
| 4 |
Moscow |
84 |
| 5 |
Delhi |
81 |
| 6 |
Sao Paulo |
75 |
| 7 |
Milan |
52 |
| 8 |
Buenos Aires |
50 |
| 9 |
Madrid |
48 |
| 10 |
London |
36 |
| 10 |
Paris |
36 |
| 12 |
Toronto |
32 |
| 13 |
Amsterdam |
25 |
| 13 |
Los Angeles |
25 |
| 15 |
Berlin |
24 |
| 16 |
Montreal |
23 |
| 17 |
New York |
19 |
| 18 |
Melbourne |
17 |
| 18 |
Houston |
17 |
| 20 |
Stockholm |
15 |
Favorable Urban Planning Characteristics Associated with Intense Traffic Congestion: The worst traffic congestion was recorded in the developing world metropolitan areas of Beijing, Mexico City, Johannesburg, Moscow, Delhi and Sao Paulo. In many ways, these metropolitan areas exhibit characteristics most admired by current urban planning principles. Automobile ownership and per capita driving is low. Transit carries at least 40% of all travel in each of the metropolitan areas. Yet traffic is intense. This is due to another urban planning "success," objective, high population densities. Higher population densities are inevitably associated with greater traffic congestion (and more intense local air pollution), whether in the United States or internationally. All six of these metropolitan areas scored 75 or above, where a score of 100 would be the worst possible congestion.
The next five metropolitan areas have accomplished nearly as much from an urban planning perspective. Milan, Buenos Aires, Madrid, London and Paris all achieve more than 20% transit market shares, and their higher urban densities also lead to greater traffic congestion. Each scores between 35 and 52.
Traffic congestion is less in the next group, which includes Toronto, Los Angeles, Berlin, Amsterdam and Montreal. With the exception of Berlin, transit market shares are less, though the urban densities in all are above average US, Canadian and Australian levels. Amsterdam, the smallest metropolitan area among the 20, scores surprisingly poorly, since smaller urban areas are generally associated with lower levels of traffic congestion.
The Least Congested Metropolitan Areas: Four metropolitan areas scored under 20, achieving the most favorable traffic congestion ratings. New York scores 19, with its somewhat lower density (the New York urban density is less than that of San Jose). Even lower density Melbourne and Houston score 17, tying for the second best traffic conditions. Stockholm achieves the best traffic congestion score, at 15, despite its comparatively high density. Stockholm is probably aided by its modest size which is similar to that of Orlando (Florida).
The Houston Advantage: Perhaps the biggest surprise is Houston's favorable traffic congestion ranking.
- Houston has the lowest urban density of the 20 metropolitan areas.
- Houston has the lowest transit market share, by far, at only 1%.
- Houston also has the highest per capita automobile use among the IBM metropolitan areas.
 Yet Houston scored better than any metropolitan area on the list except for much smaller Stockholm. As late as 1985, Houston had the worst traffic congestion in the United States, according to the annual rankings of the Texas Transportation Institute. Public officials, perhaps none more than Texas Highway Commission Chair and later Mayor Bob Lanier led efforts to improve Houston's road capacity, despite explosive population growth. Their initiatives paid off. By 1998, Houston had improved to 16th in traffic congestion in the United States. The population growth has been incessant, so much so that Houston has added more new residents since 1985 than live in Stockholm and more than half as many as live in Melbourne. While Houston had slipped to 11th in traffic congestion by 2007, the recent opening of a widened Katy Freeway and other improvements should keep the traffic moving in Houston better than in virtually all of the world's other large metropolitan areas. Yet Houston scored better than any metropolitan area on the list except for much smaller Stockholm. As late as 1985, Houston had the worst traffic congestion in the United States, according to the annual rankings of the Texas Transportation Institute. Public officials, perhaps none more than Texas Highway Commission Chair and later Mayor Bob Lanier led efforts to improve Houston's road capacity, despite explosive population growth. Their initiatives paid off. By 1998, Houston had improved to 16th in traffic congestion in the United States. The population growth has been incessant, so much so that Houston has added more new residents since 1985 than live in Stockholm and more than half as many as live in Melbourne. While Houston had slipped to 11th in traffic congestion by 2007, the recent opening of a widened Katy Freeway and other improvements should keep the traffic moving in Houston better than in virtually all of the world's other large metropolitan areas.
Photo: Freeway in Houston
A just-released report by the Institute of Transportation Studies at the University of California-Berkeley finds that the ridership projections prepared by Cambridge Systematics (CS) for the California high speed rail system are "not reliable."
Authors Samer Madanat (director of ITS-Berkeley and a professor of civil and environmental engineering), Mark Hanson (UC-Berkeley professor of civil and environmental engineering) and David Brownstown (chair of the Economics Department at UC-Irvine) essentially reported that the projections had such large error margins that the system could either lose a lot of money or make a lot of money:
... the combination of problems in the development phase and subsequent changes made to model parameters in the validation phase implies that the forecasts of high speed rail demand-and hence of the profitability of the proposed high speed rail system-have very large error bounds. These bounds, which were not quantified by CS, may be large enough to include the possibility that the California HSR may achieve healthy profits and the possibility that it may incur significant revenue shortfalls.
 Biased High Speed Rail Projections: Given the overwhelming history of upwardly biased ridership and revenue projections in major transport projects, it seems far more likely that reducing the margins of error would produce projections with much smaller ridership numbers and major financial losses. Major research by Oxford University professor Bent Flyvbjerg, Nils Bruzelius (a Swedish transport consultant) and Werner Rottenberg (University of Karlsruhe and former president of the World Conference on Transport Research) covering 80 years of infrastructure projects found routine over-estimation of ridership and revenue (Megaprojects and Risk: An Anatomy of Ambition Biased High Speed Rail Projections: Given the overwhelming history of upwardly biased ridership and revenue projections in major transport projects, it seems far more likely that reducing the margins of error would produce projections with much smaller ridership numbers and major financial losses. Major research by Oxford University professor Bent Flyvbjerg, Nils Bruzelius (a Swedish transport consultant) and Werner Rottenberg (University of Karlsruhe and former president of the World Conference on Transport Research) covering 80 years of infrastructure projects found routine over-estimation of ridership and revenue (Megaprojects and Risk: An Anatomy of Ambition ). The evidence is so condemning that Dr. Flyvbjerg has referred to the planning processes for such projects as consisting of "strategic misrepresentation" and "lying" (his words) to advance projects that might not otherwise be implemented. ). The evidence is so condemning that Dr. Flyvbjerg has referred to the planning processes for such projects as consisting of "strategic misrepresentation" and "lying" (his words) to advance projects that might not otherwise be implemented.
Broad Concern about the Reliability of California High Speed Rail Projections: The University of California report joins other reports that have questioning the veracity of the Cambridge Systematics projections. During the run-up to the 2008 statewide bond issue, the California Senate Transportation and Housing Committee, chaired by Senator Alan Lowenthal (D-Long Beach) indicated concerns. Illustrating continuing concerns, the committee commissioned the University of California study.
Doubts have been expressed by the California Legislative Analyst and the California State Auditor. The Reason Foundation Due Diligence Report, authored by Joseph Vranich and me in 2008 estimated the ridership projections to be at least 100% high (see High Speed Rail: Untimely Extravagance presented at the Heritage Foundation last week in Washington).
Investment Grade Projections Far Lower: The Cambridge Systematics ridership projections publicized that were used in the statewide bond election were more than 150% above the "investment grade" projections that had been produced by Charles Rivers Associates for the California High Speed Rail Authority a decade ago. Even "investment grade" projections can be high, as the recent bond default and bankruptcy of the Las Vegas Monorail indicates. In that case the "investment grade" ridership projections were 150% above the actual achieved average, nonetheless bond holders lost their investments. (Our 2000 report accurately projected the Monorail ridership).
Undermining GHG Emissions Reduction Claims: Meanwhile, the California high speed rail proposal has come under criticism with respect to its environmental claims. The high speed rail line has been promoted as a means for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the state. Yet another recently released University of California report indicates that it could take as long as 71 years to save enough GHG emissions by attracting airline passengers and drivers to cancel out the emissions produced in constructing the project. More defensible ridership projections could lengthen this period considerably.
Response to Criticism: The body of the University of California high speed rail study is 10 pages, followed by approximately 40 pages of comments and response by Cambridge Systematics and a letter from the California High Speed Rail Authority requesting that the University of California authors to consider the comments. This review is performed by the University of California authors, as they reject virtually all Cambridge Systematics criticisms in the final four pages of the report.
Photograph: Cover of Megaprojects and Risk: An Anatomy of Ambition
|

 "High Rise or House with Yard" stands alone in claiming that New York City is less costly than its suburbs. The most recent (and authoritative) ACCRA cost of living index for Brooklyn is a
"High Rise or House with Yard" stands alone in claiming that New York City is less costly than its suburbs. The most recent (and authoritative) ACCRA cost of living index for Brooklyn is a  Yet Houston scored better than any metropolitan area on the list except for much smaller Stockholm. As late as 1985, Houston
Yet Houston scored better than any metropolitan area on the list except for much smaller Stockholm. As late as 1985, Houston  Biased High Speed Rail Projections: Given the overwhelming history of upwardly biased ridership and revenue projections in major transport projects, it seems far more likely that reducing the margins of error would produce projections with much smaller ridership numbers and major financial losses. Major research by Oxford University professor Bent Flyvbjerg, Nils Bruzelius (a Swedish transport consultant) and Werner Rottenberg (University of Karlsruhe and former president of the World Conference on Transport Research) covering 80 years of infrastructure projects found routine over-estimation of ridership and revenue (
Biased High Speed Rail Projections: Given the overwhelming history of upwardly biased ridership and revenue projections in major transport projects, it seems far more likely that reducing the margins of error would produce projections with much smaller ridership numbers and major financial losses. Major research by Oxford University professor Bent Flyvbjerg, Nils Bruzelius (a Swedish transport consultant) and Werner Rottenberg (University of Karlsruhe and former president of the World Conference on Transport Research) covering 80 years of infrastructure projects found routine over-estimation of ridership and revenue (











