
The proposed Chicago Transit Authority (CTA) fare increase and service cuts for next year are indicative of transit’s recurring budgetary problems, and not only in Chicago but nationwide. But in the Windy City, these moves have elicited an understandably negative public reaction since the city of Chicago depends on transit about as much as any city besides New York.
CTA, like other transit agencies around the nation routinely, claim that fare increases and service cuts are necessary due to under-funding. Transit budget crises seem to come as often as Presidents day in many places and more often than February 29 (every four years) virtually everywhere.
If under-funding were the primary problem, then an examination of historic trends would indicate that the money available to transit had declined (after adjusting for inflation) relative to ridership. But in nearly all cases, including both the CTA and the national data, this is far from the truth.
Cost Escalation at CTA: Despite its storied history as one of the nation’s premier transit agencies, CTA has suffered heavy ridership losses since its modern peak in 1979. A principal reason for this decline was a series of devastating fare increases that would not have been necessary if costs had been maintained within inflation. In 2007, CTA spent 13% more (inflation adjusted) to run its buses and trains than in 1979. That would be fine if ridership had risen 13% (or more), since then both riders and taxpayers could feel that they had obtained value for money. However, ridership dropped by more than 2 percent. If CTA had kept its costs per passenger within inflation, it would have at least $400 million more each year, and would have no need to consider fare increases or service reductions.
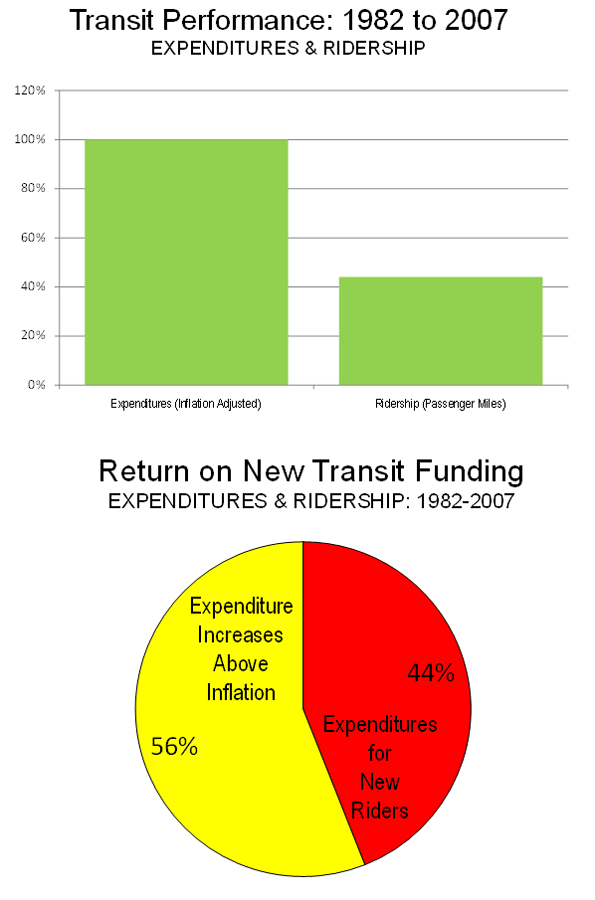
National Transit Cost Escalation: Between 1982 (the last year before the federal gas dedicated gas tax for transit) and 2007, national transit ridership (passenger miles) rose 44% percent. At the same time, transit expenditures, adjusted for inflation, rose 100%. This means that each new inflation adjusted $1.00 for transit delivered $0.44 in new value (additional ridership). If transit had kept expenditures growth within inflation, there would have been in excess of $13 billion in 2007 (See Note).
In contrast, the price (or cost) of most products and services rise about with the rate of inflation or slightly more or less. Over the same period of time, automobile and airline costs per passenger mile have declined, producing more than $1.00 in value for each new inflation adjusted dollar. Food costs have declined 3 percent relative to inflation, energy costs have declined 2 percent relative to inflation and housing costs have risen 1 percent relative to inflation.
Transit’s Intractable Fiscal Problem: Transit is incapable of producing ridership increases that coincide with its funding increases because of its structure. Transit is a monopoly, and an unregulated monopoly incapable of managing itself effectively. Private monopolies, such as electric utilities, are routinely regulated. Economic theory generally holds that monopolies are to be avoided, because of their power to violate the interests of consumers by passing on higher than necessary prices and substandard service. No responsible government would think of granting a monopoly to a private company without exercising regulatory control to ensure that the company does abuse its position of power.
Before the wide availability of subsidies to transit, there were private companies, which could not raise fares or cut service without regulatory review and approval. It was not the best possible system, but it was designed to principally serve consumers. But government is different. There are no commissions set up to regulate government monopolies, like transit.
Competitive Incentives: The antidote to monopoly is competition, and transit costs cannot be controlled without it. There is a successful model. Transit agencies can competitively bid and competitively contract bus routes for limited periods of time, requiring firms to supply services they specify. The public agency continues to draw the routes, establish the timetables and set the fares. In a number of cases, competitive contracting has lowered costs and reduced the rate of cost increase.
In Los Angeles, our efforts led to carving a new transit district (Foothill Transit) out of the old public monopoly (the Southern California Rapid Transit District). Other services were transferred from the public monopoly to be administered by the city of Los Angeles. In each case, the transferred services were competitively contracted, and evaluation reports put the savings at more than 40%. Similar results have been achieved in Denver and San Diego, where approximately 50% of bus services are now competitively contracted. In Denver, the competitive contracting program was established by state legislation, while in San Diego, local officials introduced the program to gain control of rapidly escalating costs. More than a decade ago, my report for the Metropolitan Transit Association showed that substantial savings could be achieved at CTA through competitive contracting without requiring employee layoffs or give-backs.
Competitive contracting has even spread to commuter rail systems, such as in San Diego, Dallas-Fort Worth, Miami, Boston and Los Angeles. However, for all of these savings, competitive contracting accounts for only a small share of transit services in the United States.
The Antithesis of Cost Effectiveness: There remains strong resistance by the special interests that control transit, from the managers to the employees to vendors. Within a couple of years, the California legislature caved to lobbying from transit interests, including the transit unions, and outlawed the kinds of cost reducing reforms that had created Foothill Transit. This is despite the fact that not a single penny in wages or benefits had been taken away from a single transit worker.
Perhaps the most brazen case was when the Denver transit agency approached the state legislature in the early 1990s seeking repeal of the competitive contracting bill, claiming that it was costing the agency more than if the services were provided by its own employees. It later was revealed that the analysis had compared the internal costs of operations with the competitively contracted costs of operations and capital (buses and facilities). It was even worse than that. The cost of the competitively contracted buses was amortized at a rate more than double the normal accounting standard. After this misleading initiative, the legislature expanded the competitive contracting requirement.
The resistance of monopoly transit interests to competitive contracting is understandable. People and organizations generally tend to look out for their own interests first and unregulated monopolies can do so with a vengeance. Without the countervailing force of competition (or, less effectively, regulation) their financial demands prevail over the interests of the riders and taxpayers, without whom there would be no reason for transit to exist.
One result is that when major transit expansions are chosen, the approaches that cost the most per passenger are often selected. The classic case is the selection of rail technologies over bus technologies, which are usually far more cost-effective given the modest transit volumes in the United States. Instead we often choose rail systems that cost more on an annual basis than it would cost to lease each new transit customer a car in perpetuity. Sometimes the cost equals that of an economy car, other times it could be a Lexus.
Another contributing factor has been transit wages and benefits, both for managers and operating employees. These have risen far faster than in competitive markets, whether unionized or not. Other costs have risen as well, from capital costs to the costs of administration. The present monopoly situation effectively establishes a public policy objective of maximizing transit costs per passenger. The focus should be on maximizing ridership by minimizing expenditures per passenger.
Internal Reforms Do Not Survive: There is always the potential for internal reform. One of the most sweeping of such programs was implemented by Chicago’s Mayor Jane Byrne in the early 1980s. She forced major cost reductions at CTA. However, after she left, costs resumed their upward trend. It is difficult, if not impossible, to sustain the political will to control transit costs without the incentives of competition.
Overseas: Perhaps surprisingly, the conversion to competition has been widespread overseas. Virtually all of the world’s largest public bus systems take this approach. Transport for London (formerly London Transport) is competitively bid. Between 1985 and 2000, the costs per mile of service declined more than one-half, adjusted for inflation. Much the same has occurred in Socialist Scandinavia. All Copenhagen bus service is competitively bid. Stockholm not only bid its bus service, but also saved money by competitively bidding its metro (subway) system. Commuter rail lines are being competitively bid in Germany, as are entire bus systems in Adelaide and Perth in Australia. In all of these cases, the public has gained by lower costs, expanded services and generally lower fares than would have otherwise been the case. In the United States, however, the surviving public monopoly structure skims more than half of the new money off the top, leaving less than half for the riders and taxpayers.
Why This is Important: All of this is relevant because there is a sense that transit will play a much larger role in the future. Virtually none of the analysis exhibits any understanding of the dynamics that rule transit expenditures. For example, the contentious Moving Cooler presumes that transit expenditures will rise within the inflation rate and, as a result, expects romantically unachievable increases in ridership.
This is wishful thinking of the worst kind. Congress, the state and the nation’s transit agencies have studiously avoided any sort of analysis that would compare transit costs to inflation. They cannot be relied upon to set things right since they will not confront the special interests that control transit.
Instead, American transit agencies spend more without a corresponding increase in ridership. New money made available to transit loses value like the depreciating currency of a hyper-inflating economy. Washington, state governments and local governments can throw a lot more money at transit. They seem incapable however of producing a corresponding increase in ridership.
Note: National expenditures calculated from the governments database of the United States Bureau of the Census. Ridership from the American Public Transportation Association. Chicago ridership and operating cost data from the American Public Transportation Association and the US Department of Transportation Federal Transit Administration National Transit Database. Financial data adjusted to 2007$ using the Consumer Price Index.
Wendell Cox was appointed to three terms by Mayor Tom Bradley to represent the city of Los Angeles on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission (LACTC), which was the principal transit and highway policy body in the nation’s largest county. As the only LACTC member who was not an elected official, he chaired the Service Coordination Committee, which established the procedures that led to the establishment of Foothill Transit. He also chaired two American Public Transit Association national committees (Governing Boards and Policy & Planning).













I think this is an
I think this is an informative post and it is very useful and knowledgeable. therefore, I would like to thank you for the efforts you have made in writing this article. propertykita
Interesting idea about
Interesting idea about openning individual routes to contracts. Some thoughts:
(1)
Relinquishing public money to private firms makes me nervous. I think there is often a severe lack of accountability once a contract is signed. In GA, for instance, a private company has been hired to operate municiple services in a few suburban areas (garbage pick-up, etc). The belief was that an entrepreneurial approach to service would yield lower costs and, thus, lower taxes. Mid-contract, people want to know if they are paying too much. The firm will not reveal its profits. The public has no way of knowing if they are being "over-taxed" by the company and no recourse except to let the contract run out.
For short-term contracts this might not be a huge loss. Two or three years of over-paying for service. But the incentive for lengthier deals ("Buy in bulk, save more!") could lure tax-payers into 10, 15, or 25 year contracts. Longer terms increase the risk of encountering some financial hardship during the contract. What does a city do, for example, when recession strikes and agreed-upon payments cannot be made? Instead of being able to scale back garbage pick-up (as would be the case in a government-run system), the community must scale back on non-contracted spending... like education.
Certainly there are some inefficiencies in government. But I believe that extra cost is returned in the form of accountability and flexibility.
(2)
"Between 1982 (the last year before the federal gas dedicated gas tax for transit) and 2007, national transit ridership (passenger miles) rose 44% percent. At the same time, transit expenditures, adjusted for inflation, rose 100%. This means that each new inflation adjusted $1.00 for transit delivered $0.44 in new value (additional ridership)."
I think the more important measure might be passenger trips since riders on CTA pay by the trip, not by the mile. I understand that you are talking about value returned to the customer ("how far does the train carry me?"), but this calculation ignores the farebox and warm bodies. If, for example, people are travelling shorter distances on average, then a 44% increase in passenger miles would equate to a greater-than-44% increase in trips. The number of increased riders might be so great that the increase in expenditures would appear reasonable.
Were service times extended during this period to facilitate late-night trips? Were more vehicles placed on routes to decrease average wait-time? There are a number of dimensions not included in this equation where value could have been returned to the customer.
This is a great post. I like
This is a great post. I like this topic.This site has lots of advantage.I found many interesting things from this site. It helps me in many ways.Thanks for posting this again.
cell phone spy
Thanks for this great post,
Thanks for this great post, i find it very interesting and very well thought out and put together. I look forward to reading your work in the future. Natural supplement
And the assumption...
And the assumption here is that transit is planned in a way that makes sense. That the planners did extensive studies of the region and figured out where people lived and where they worked, and built transit lines to connect those two places.
Here in San Jose, we built a Light Rail that connects businesses to the central San Jose metro area, and doesn't go anywhere near anything zoned Residential. This is because the city planners were train freaks who wanted to see the train go by City Hall every day, and used "If You Build It They Will Come" as their guiding philosophy.
Ѕomeone essentiallу ɦelp
Ѕomeone essentiallу ɦelp to makoe critically articles I'd state. ҬҺat is the vefy firѕt time I frequdnted youг website page and to this point? ӏ amazed wwith the analysis yyou made to make this actual post increԀible. jual korset tulang belakang