Chicago's violent crime problem can be understood through this formula:
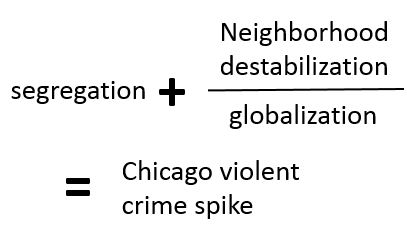
It's a simplistic, reductionist, even crude, but it explains the roots of Chicago's crisis as well as anything.
It has been particularly grueling time in Chicago this recently. We experienced the murders of at least ten Chicagoans, including two girls, age 12 and 11, shot within 30 minutes of each other in different locations, and a 2-year-old boy. Once again, Chicago is thrust into the spotlight as President Donald Trump spoke of "two Chicagos" and renewed his pledge to send some kind of federal assistance to deal with the violence (note: you may have seen me refer to "two Chicagos" before, but I'm definitely uneasy with our current President making even starker distinctions between them). And with each new story of violence, of television and newspaper reporters being sent out to document another life lost, of an expression of heartbreak from a grieving parent, we ask ourselves, "how did it get this way? How do we solve it?"
In many respects the violent crime wave is a reaction to the same trends that got our president elected, but coming from even deeper and longer lasting strains of dislocation and disenfranchisement. It's also a set of unintended consequences related to very specific policies undertaken by the city itself. While Chicago's experience is rather unique among American cities, other cities that exhibit similar traits are seeing the same spike as well. In each case, the spike is decades in the making.
Segregation
It starts with segregation. Chicago's leaders during the early years of the twentieth century were the innovators of a segregation system that plagues the city to this day. Natalie Moore, South Side bureau reporter for Chicago public radio station WBEZ and author of The South Side: A Portrait of Chicago and American Segregation, noted the pervasiveness of segregation in Chicago in this interview with the Chicago Tribune:
"People know that segregation exists, but they don't always think about it," said Moore, WBEZ's South Side Bureau reporter and the author of "The South Side: A Portrait of Chicago and American Segregation." "It's like air and water: You just kind of live it, but you don't think about it."
And how was it established? Tribune reporter Jeremy Mikula and Moore go on:
"The institutional racism Moore charts in the book goes back generations and has its roots after the start of the Great Migration. Restrictive covenants prevented African-Americans from moving outside the city's historic Black Belt until U.S. Supreme Court cases such as Hansberry v. Lee (1940) and Shelley v. Kraemer (1948) eliminated such restrictions in housing.
Through that time, Moore writes, "the city designed a way for blacks to not fully participate in the freedoms of the North," and later formulated subtle policy decisions that can still be felt today, she said.
"All the things from redlining to the Home Owners' Loan Corporation to blockbusting to white flight, there are so many things that happened in the 20th century that have lingering effects," Moore said. "It's never been about white people want to live there and black people want to live there. This is where the history is really important for us to understand."
Emphasis added.
Tools were developed and employed to create a segregated Chicago -- restrictive covenants, redlining, exclusionary zoning, urban renewal, interstate highway development, public housing development, aggressive policing tactics and a judicial system that exploits inequality -- and those tools are foundational to our understanding of the way the city operates today.
Chicago is not alone in its history of segregation, nor is it alone in its current spike in violent crime. In fact, it may not even be the worst. In late 2016, USA Today reported on the nation's most violent cities, based on 2015 FBI violent crime data. Chicago was not among the top ten. The list was headed by St. Louis, followed by Detroit, Birmingham, Memphis, Milwaukee, Rockford, IL, Baltimore, Little Rock, AR, Oakland and Kansas City. What's dispiriting is the number of violent cities that are also among the most segregated. St. Louis, Detroit, Birmingham, Memphis, Milwaukee and Kansas City are on most lists of highly segregated cities, as well as Chicago, Indianapolis, Cleveland, Cincinnati and Philadelphia. Nearly all have seen violent crime increases.
Neighborhood Destabilization
So Chicago became a highly segregated city, with large numbers of blacks cut off from the economic and social networks necessary for upward mobility. Old segregated spaces increasingly became impoverished spaces, as former white neighborhoods became new segregated spaces. Concentrated poverty became super-concentrated with the development of the public housing in Chicago, and by the '80s and '90s Chicago was notorious for two features of its segregated system: 1) a gigantic collection of gangs operating as organized criminal enterprises; and 2) a depraved and dysfunctional public housing system, which also served as a base for gang activity. To many, the dysfunction of Chicago's public housing was crystallized in the story of the murder of Eric Morse, a 5-year-old taken to a vacant 14th floor Ida B. Wells public housing complex apartment by two preteens, and dropped to his death because he would not steal candy for them. The city, and the nation, was outraged.
It's at this point that Chicago made a significant departure from other cities and pursued three policy choices that impacted the stability of its neighborhoods. First, it made a concerted effort to lock up the leadership of the gang hierarchy, intent on "cutting off the head" of the gangs. Second, the city recognized the failure of its public housing system, and elected to dismantle its most troublesome projects through its Plan for Transformation. Third, in a cost-saving measure, the city closed nearly 50 public schools, with nearly all being in the highly segregated south and west sides.
Each played a role in undermining the stability of Chicago's south and west side neighborhoods, sending them into the violent crime spiral we see today.
In the mid-'90s, Chicago police worked with the U.S. Attorney's office to establish Operation Headache. At the time the Chicago drug trade was largely controlled by gangs that were more akin to organized crime syndicates than gangs in the conventional sense. The Gangster Disciples, the Black Disciples, the Vice Lords and the Latin Kings covered large parts of the city and developed distribution networks and open-air drug sales areas, and law enforcement found the problem nearly intractable. Operation Headache represented a shift in tactics designed to bring them down. Rather than focus on lower-level drug dealing youth who cycled in and out of the criminal system, they chose to go after gang leaders in an effort to destabilize them, and it was successful:
"The first wave of convictions stemming from Operation Headache came in March 1996. But the biggest, most symbolically meaningful blow to the Gangster Disciples was delivered in May 1997, when Hoover was convicted of 42 counts of conspiracy to distribute drugs, received a sentence of six life terms, and was transferred to a supermax prison in Colorado, where his cell was located several stories underground and his ability to communicate with the remnants of his gang were severely constrained. Soon, the GDs in Chicago had been all but neutralized, and the authorities shifted their attention to decapitating the city’s other major drug organizations, the Black Disciples and the Vice Lords.
Over the course of a roughly 10-year stretch starting in the mid-1990s, leaders from the GDs, the Vice Lords, the Black Disciples, and to a lesser extent, the Latin Kings were successfully prosecuted and taken off the street. The top-down assault appeared to work as Safer and his colleagues had hoped: violent crime in Chicago began to decline, with the city’s murder total dropping from a high of 934 in 1993 to 599 10 years later."
Beginning in 2000, the Chicago Housing Authority moved out public housing residents from developments that looked like this:

and demolished them. The goal was to replace them with less concentrated developments that would be integrated with their surrounding communities that looked more like this:

or like this:

The critical difference would be, however, that the CHA would now pursue a mixed-income approach to public housing development to address the city's segregation problems and poverty concentration. To do that, a third of residential units in new developments would be reserved for public housing residents, another third would be developed as affordable units for working-class and middle-class residents, and the last third would be sold or rented as market-rate properties.
Just as Operation Headache was successful in its early stages, so was the Plan for Transformation. CHA worked closely with the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development to tear down the old public housing towers, and completed developments that did indeed appear more integrated into the surrounding neighborhood and fulfilled the mixed-income character that people desired. By the mid-2000s both policies looked to be successful elements in the remaking of Chicago.
But there were unintended consequences that law enforcement and housing officials did not see. Violent crime in Chicago dropped to historic lows by 2005, leveled off for a few years, and started trending upward. One reason cited? Law enforcement became a victim of its success:
"While experts say the Latin Kings, a Hispanic gang, continue to run a large and rigidly organized drug-selling operation on Chicago’s West Side, the majority of Chicago residents who call themselves gang members are members of a different type of group. Rather than sophisticated drug-selling organizations, most of the city’s gangs are smaller, younger, less formally structured cliques that typically lay claim to no more than the city block or two where they live. The violence stems not from rivalries between competing enterprises so much as feuds that flare up with acts of disrespect and become entrenched in a cycle of murderous retaliation.
Many close observers of Chicago’s violence believe that, as well-intentioned as it was, the systematic dismantling of gangs like the Disciples led directly to the violence that is devastating the city’s most dangerous neighborhoods in 2016. Taking out the individuals who ran the city’s drug trade, the theory goes, caused a fracturing of the city’s criminal underworld and produced a vast constellation of new entities that are no less violent, and possibly even more menacing, than their vanquished predecessors."
Meanwhile, CHA was successful in the dismantling of old projects, but had limited success in the development of new ones, especially when trying to implement the mixed-income model. In 1999, CHA committed to finding replacement housing for all public housing residents who would be displaced by the demolition, counting on their ability to construct mixed-income developments. However, they soon ran into several challenges. Private developers were finding it difficult to obtain financing for mixed-income developments, despite federal, state and local commitments. But more importantly, market-rate buyers and renters, and even buyers and renters in the affordable range, showed little desire to share space with public housing residents.
This curtailed CHA's ability to construct new developments, and forced them to rely much more heavily on Housing Choice Vouchers (HCVs, commonly referred to as Section 8 vouchers) to provide housing for former public housing residents. An April 2011 report by CHA found that of the 16,500 public housing family households they committed to developing mixed-income units for, only 20% were actually in such developments. There were 36% living in CHA projects that weren't demolished, and 44% received HCVs and were living wherever their voucher would take them.
Where did voucher holders go? Generally to working-class black neighborhoods further south or west of former public housing sites on the south and west sides. Many Robert Taylor and Stateway residents left Bronzeville and moved to the Englewood and Auburn-Gresham neighborhoods further south; many Horner and Rockwell residents left the near west side and Garfield Park and moved to Austin, further west.
The last straw was the closure of schools by the Chicago Public Schools in 2013. By the mid-2000s, for anyone who cared to note it, there was growing evidence of conflict within the city's public schools as children new to various neighborhoods competed with children of long-time residents. At the same time the school system continued down its own budget spiral as the service delivery costs went upward and pension obligations went unmet. That forced consideration of closures by CPS, much to the dismay of community residents familiar with the disruption caused by gang disorganization and an influx of poor residents. Not only would the education of students be compromised by the closings, they argued, but the conflicts seen as voucher-holding residents moved into their communities would arise again. New school boundaries would put combustible mixes of vulnerable children in new and dangerous environments.
Globalization
The election of Donald Trump as president has brought sharp focus to the polarization of our nation by economics, class and geography. Well-educated and high-skilled workers are succeeding in today's economy; less-educated and lower-skilled workers are failing. A lot of people view this within the context of our nation's white working class in small cities and rural areas, but the same applies to blacks in cities like Chicago as well.
I'm going to plagiarize myself and pull some things about Chicago I wrote last year, when I saw six distinct categories of neighborhoods in the city. Here's the map:

Gentrified Communities (dark green): Former middle and working-class neighborhoods that have firmly become well-to-do neighborhoods over the last 30 years or so. Home to a substantial amount of Chicago's walkable urbanism inventory. Transit supported and amenity rich.
Gentrifying Communities (light green): Historically similar to the adjacent gentrified communities, but part of a second or third wave of growth that emanated from the first group. Almost as affluent and educated as the first group, and quickly catching up, but not quite there yet.
Frontline Communities (yellow): Largely working-class neighborhoods that may be experiencing development pressure generated in the gentrified/gentrifying communities. People in the above two areas may identify with communities here as places for authentic ethnic dining or shopping. Less wealthy and with more minorities than the gentrified/gentrifying communities, but less than those on its outer flank. In Chicago, at least, fear of the prospects of gentrification here may exceed reality.
Stable Prosperous Communities (gold): Middle-class neighborhoods that sprouted in the city at the advent of the suburban era and have changed little since. Single-family home oriented and auto-oriented. In Chicago, home to many city workers who must remain in the city due to residency requirements. Rapidly growing older in its makeup.
Transitioning Communities (orange): Structurally similar to the stable prosperous communities, but more deeply impacted by one or two transitions. Some are receiving a large influx of new minority residents, largely Latino. Others are experiencing a huge outflow of middle-class families, largely African-American. Those experiencing the Latino influx are becoming younger and less affluent; those experiencing the African-American outmigration are being hollowed out, leaving behind large numbers of older and younger less affluent residents.
Isolated Communities (brown): Impoverished areas of the city. Middle-class white residents left here in the '50s and '60s, replaced by middle-class and working-class blacks who bore the brunt of job loss in the subsequent decades. Plenty of walkable urbanism exists here, but demolition means it's fading away.
Here are a few data pieces I gathered for each of the categories I identified (you can click to see bigger):
Looking at the map, the green and light green neighborhoods have been Chicago's winners in today's global economy. The gold neighborhoods have been doing reasonably well. Depending on your perspective, the yellow neighborhoods are threatened with gentrification encroachment, or have a reasonable expectation of upcoming revitalization. The orange and brown neighborhoods? They're not doing so well. They're the ones largely impacted by Chicago's century-old segregation legacy, or in various stages of instability via the actions undertaken over the last 25 years.
Chicago's rigid segregation patterns set the stage economic divergence before globalization did, but globalization made it worse. And in the aftermath of the Great Recession, when globally connected communities returned to their upward trajectory, troubled communities sunk further into the abyss.

Chicago's violent crime spike will not be solved with National Guard troops patrolling the streets. It will not be solved with greater emphasis on gun control laws. It will not be solved by a wholesale reform of the Chicago Police Department, which has just come out of a year-long investigation by the U.S. Department of Justice that excoriated its "excessive force, lax discipline and bad training." All of these measures would have some incremental impact on violent crime. Crime would go down, if only temporarily. However, these measures treat the symptom. None would do anything to address root causes and eliminate the problem for good.
There is an answer to Chicago's madness. It would not solve the problem overnight, but it would have the potential to solve it for the long term. I'll outline it in my next blog post later this week.
Pete Saunders is a Detroit native who has worked as a public and private sector urban planner in the Chicago area for more than twenty years. He is also the author of "The Corner Side Yard," an urban planning blog that focuses on the redevelopment and revitalization of Rust Belt cities.
Top photo: A body is removed from the scene after a man was shot and killed in the 3000 block of West 53rd Place in Chicago. — Anthony Souffle, Chicago Tribune, April 13, 2014



















