NewGeography.com blogs
Despite the success of the Main St. line, I've been concerned for a long time now that the next set of rail lines will essentially bankrupt Metro while providing minimal benefit (except for possibly the Universities line, which has moderate benefits, but may not get built anytime soon because of the money drain of the other lines being built first). Now the Coalition On Sustainable Transportation (COST) has come out with the numbers from other cities (especially Dallas) that don't bode well for Houston at all. Some key excerpts (I know it's a lot, but there are some really good points in here):
---------------
For example: Dallas will pay increasing debt service for many years and has 30 plus year bonds and commercial paper for its almost $4 billion of debt. Their debt service is considered annual operating costs in the chart below, because: By the time current bonds are paid, the rail system will be at the end of its service life and will need replacement through the creation of a new round of bonds, continuing this high bond expense for as long as the system operates. While other Texas cities have not yet reached this Dallas level of bond debt and expense, Houston is rapidly moving in the same direction and Austin’s planning is pointing in this direction. Currently Dallas’s debt service is about 3 times Houston’s and almost 40 times Austin’s.
...
One may look at the data in the table above in many ways, but, none of the conclusions seem to be positive for rail transit. Dallas, Houston, San Antonio and Austin are all among the top 20 fastest growing major cities in the nation. However, the three cities with various levels of rail transit, Dallas, Houston and Austin, all have declining transit ridership trends and have fewer absolute transit riders today than they had a dozen years ago. They have spent billions to implement and promote transit with a heavy focus on rail transit.
...
These data highlight a number of broader Texas Metro Area negative transit trends:
1. Metro areas with more rail transit have significantly higher costs and higher taxpayer subsidies per ride.
2. Metro areas with more rail transit have fewer total transit boardings per capita.
3. Metro areas with higher densities have fewer transit riders (boardings) per capita.
4. Dallas has the largest population and greatest population density but the least cost effective transit system: Higher cost per ride (boarding) and fewer boardings per capita.
5. Increasing the proportion of a region’s transit funds being spent on rail transit leads to less cost effective overall transit and degraded transit for the majority of transit riders who still ride busses.
Some Major Texas City Metro Areas comparisons/observations regarding transit data:
1. Dallas-Ft. Worth Metro’s population is more than 3 times San Antonio’s and Dallas’ annual transit operating expense is 4.4 times San Antonio’s but Dallas has only 1.6 times the transit ridership of San Antonio.
2. Dallas-Ft. Worth Metro’s population is 3.8 times that of Austin and Dallas’ annual transit operating expense is 3.7 times the transit expense of Austin but Dallas-Ft. Worth has only 1.9 times Austin’s ridership.
3. Dallas has the most invested, more than $4 billion, in light rail and it has the highest cost per transit ride at 2.8 times San Antonio’s costs and almost 2 times Austin’s. Dallas has the least boardings per capita, about one-half of San Antonio and Austin.
4. San Antonio’s bus only transit system has 1.2 times Austin’s ridership but only 82% of Austin’s annual operating expense.
5. San Antonio’s ‘cost per transit rider’ is about one-third of Dallas-Ft. Worth’s and San Antonio has 2 times as many transit riders per capita as Dallas-Ft Worth.
6. Dallas’ 2011 net debt service (principal and interest) budget of $153 million is greater than San Antonio’s total 2011 budgeted operating costs of $141.3 million and almost as much as Austin’s $168.2 million.
...
It is no surprise that Dallas has hit a transit financial wall causing it to pause and curtail, at least temporarily, further light rail expansion. It seems, the more light rail Dallas implements, the more inefficient and expensive its transit becomes. This is an often occurring trend when regions implement rail transit and is a serious problem trend now developing in Houston and Austin. The result is overall degradation of transit service as exorbitantly expensive rail transit and resulting debt absorb increasingly higher percentages of transit funds. This, in turn, results in increasing transit fares and reductions in bus service which have disproportionately negative quality-of-life impacts on lower income citizens. Almost everyone forgets that the majority of transit riders still ride busses even after such massive investments in rail transit such as in Dallas or in Portland, the Mecca of train transit, where well over one-half of the transit rides are on busses. More importantly, this wasteful spending on ineffective trains ‘bleeds dry’ taxpayer funds which could be used to make positive contributions in serving communities’ many, higher priority needs for all citizens. (like express commuter bus services from all neighborhoods to all job centers, as I've been advocating)
...
Much experience has shown that once a cycle of high cost rail transit is implemented, the agency becomes heavily burdened with debt for a very long time. It is highly probable that the very high debt service (principle and interest) will become a permanent and major part of the transit agency’s annual operating costs. When one issue of bonds is paid down, it becomes time for another round of debt to replace aging equipment. This, in turn results in very poor cost effectiveness and degradation of the overall transit system as it serves fewer riders at higher costs. This high debt can never be paid-off without major increases in local taxes. Transit agencies cannot responsibly project and achieve enough ridership to make rail transit cost-effective. This has even less credibility in light of the national declining trend in the use of transit and the fact that the use of transit in Texas’ major metro areas has a declining trend over the past dozen years. As Dallas and other major cities have experienced, this results in a spiraling decline in transit performance and effectiveness, degradation of mobility for low income citizens and, often, cutbacks in other higher priority city services. This results in reducing overall quality-of-life.
----------------
Is this the future we really want for Houston? Because it's not too late to stop it now, but it will be too late very, very soon, and then we will be stuck with the same harsh reality as Dallas for decades to come...
This post first appeared at Houston Strategies
We recently noted that Ryan Avent was one third right in his recent Sunday New York Times article on urban density. Avent has posted a response suggesting that it is inappropriate to use average urban densities in urban productivity analyses, as we had done, but that "weighted average densities" should be used instead. Weighted average density was not mentioned in his New York Times article.
In the interim, we were able to find the studies on urban density and productivity that seem to match those Avent refers to in his New York Times article. There are two studies concluding that doubling employment (not population) density increases productivity by six percent (Ciccone & Hall, 1996 and Harris & Ioannides, 2000), as Avent noted. Another study (Davis, Fisher & Whited, 2007) indicates that doubling employment densities could increase productivity by as much as 28 percent, also as Avent noted.
Urban and Rural Density Combined Are Not Urban Density: In contrast to Avent's preference for weighted average density, each of the studies uses average density, like with our analysis. More importantly the econometric formulas in the studies do not include an urban density variable. The density variables in all three studies include rural areas.
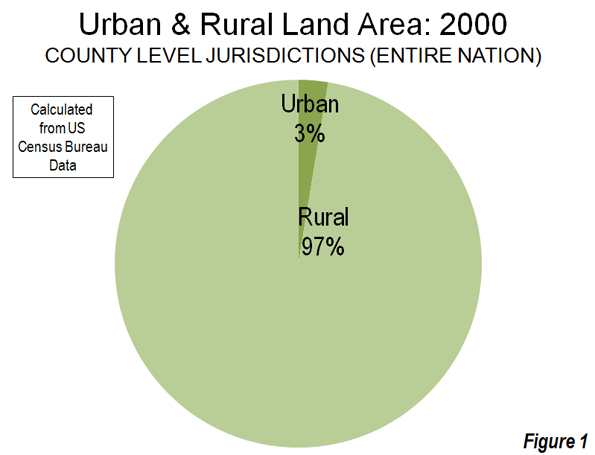
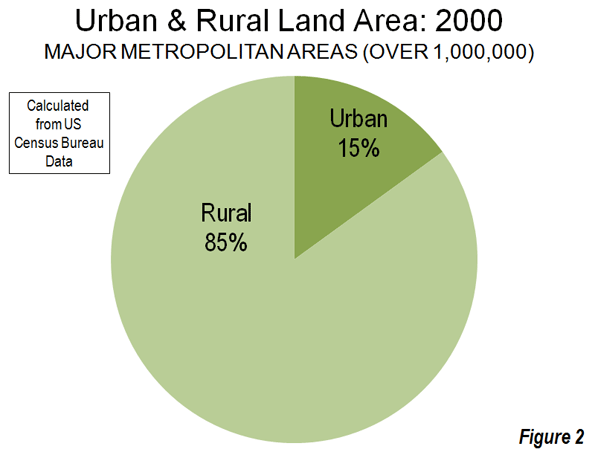
The studies use county, metropolitan area and sub-metropolitan area densities, each of which contain far more rural land than urban land. By definition, urban areas exclude rural areas and, as a result, the moment rural areas become a part of the calculation, the result cannot be urban densities. In 2000, Census Bureau data showed counties (county equivalent level jurisdictions), which comprise the entire nation, to be less than three percent urban and more than 97 percent rural (Figure 1). Metropolitan areas also have a similar predominance of rural land (Figure 1). Among major metropolitan areas (those with more than 1,000,000 population) in 2000, approximately 85 percent of the land was rural and 15 percent of the land was urban (Figure 2).
Ciccone & Hall use employment density at the county level and thus mix urban and rural densities. Harris & Ioannides use employment densities at the metropolitan statistical area or the primary metropolitan statistical area level (a sub-metropolitan designation since replaced by the more appropriately titled "metropolitan division"). Davis, Fisher & Whited use employment densities at the metropolitan statistical area level. The two studies using metropolitan areas or parts of metropolitan areas also mix urban and rural densities.
Urban Area Densities: Urban density is calculated at the urban area level, which is the area of continuous urban development. This is also called the urban footprint, which is generally indicated by the lights of the city one would see from an airplane on a clear night. Urban areas are delineated using the smallest census geographical units ("census blocks," which are smaller than census tracts) each ten years. The 2010 data will be released next year. Among urban areas, the highest density core urban area in a major metropolitan area (Los Angeles) is approximately four times the lowest (Birmingham).
Nonsensical Metropolitan Area Densities: Theoretically, metropolitan areas are labor market areas, which include a core urban area (and sometimes more than one urban area) and nearby rural areas from which people commute to work in the urban area (can be called the "commuter shed"). However, in the United States, metropolitan areas are too coarsely defined for density comparisons with one another. US metropolitan areas are composed of complete counties or, in the six New England states, complete towns. This jurisdictionally based criteria can produce metropolitan areas that are much larger than genuine labor markets in a number of cases and some that are smaller. American metropolitan areas are not spatially consistent by any functional labor market definition. Metropolitan densities are thus nonsensical, no matter what density is being measured (such as population or employment density). Among major metropolitan areas, the highest density metropolitan area (New York) is 24 times that of the lowest density (Salt Lake City), six times the maximum difference in urban area density.
Metropolitan Ireland and Happenstance: In the similarly sized San Francisco (as used by Davis, Fisher and Whited) and Riverside-San Bernardino metropolitan areas, San Francisco has 1,700 square miles of rural land, while Riverside-San Bernardino has 26,000, approximately 15 times as much. At more than 27,000 square miles, Riverside-San Bernardino covers more land area than the Republic of Ireland. The difference in population densities between metropolitan areas is determined in considerable measure by the size (land area) of the included counties, not by the number of people in cities.
If the state of California were to carve out a new county composed of western Riverside and San Bernardino counties (as Colorado created Bloomfield County in the early 2000s), the land area of the metropolitan area could be reduced 95 percent, because the remainder would not meet the criteria for inclusion in Riverside-San Bernardino. The importance of the density variable for Riverside-San Bernardino in econometric formulas would be increased many times. With only 3,100 county level jurisdictions of varying sizes, this kind of incomparability cannot help but occur. The boundaries of metropolitan areas are defined by political happenstance.
On the other hand, the nation's urban areas are built up from 7,000,000 census blocks. This permits a fine grained definition that makes urban areas appropriate for density comparisons. The definition of urban areas is beyond political fiat.
Metropolitan areas in the United States could be readily defined at the census block level, just like urban areas. Regrettably, the Office of Management and Budget missed another opportunity in the 2010 census to make the necessary criteria change. U.S. metropolitan area data is of great value for most analysis, but misleading for spatial or density analysis.
Low-Density Productivity: Subregionalizing the density and productivity analysis would pose problems. Avent uses household incomes as his standard (and we agree that cost of living differentials are important). The San Jose metropolitan area has the highest household incomes of any major metropolitan area and would therefore be among the most productive. Yet, San Jose's automobile-oriented Silicon Valley, to which much of the productivity is attributable, has a far lower employment density than the transit and pedestrian oriented cores of Manhattan and San Francisco (and yes, even not-so-transit oriented downtown Phoenix). In low-density Seattle, Microsoft's automobile oriented Redmond campus probably ranks among the most productive real estate in the country, yet its employment density (like that of Silicon Valley) pales by comparison to the higher density cores of Seattle, Phoenix, Nashville, Oklahoma City and virtually every other downtown core of a major metropolitan area.
At the End, Agreement: Avent concludes, "I just want to make sure we stop costing ourselves easy opportunities for growth." I could not agree more. It is time to abandon regulations that artificially raise housing prices, deprive households of a better standard of living, and drive them to places they would rather not live. For centuries, people have flocked to urban areas for better economic opportunities. Urban areas should be places where people can realize their aspirations, not places that repel them because it doesn't suit the interests of those already there.
Ryan Avent hits a home run, strikes out and earns a "yes, but," all in the same article ("One Path to Better Jobs: More Density in Cities") in The New York Times.
A Home Run on Housing Regulation: Avent rightly notes that the land-use and housing regulations of metropolitan areas like San Francisco have not only driven housing prices higher, but also negatively impacted economic growth. Studies in the UK, the US and the Netherlands have demonstrated that significant restrictions on land use (called smart growth or urban containment) lead to reduced employment and economic growth in metropolitan areas. His comparison to OPEC is "right on" – that metropolitan areas like San Francisco have squeezed the supply of housing, which, of course, drives up house prices, just as restricting the supply of any good or service in demand will tend to do. Avent is also right in noting that high housing prices have driven huge numbers of people out of the San Francisco Bay Area to places like Phoenix. According to the Census Bureau, nearly 2,100,000 people moved from Los Angeles, San Francisco, San Diego and San Jose between 2000 and 2009 to other parts of the country.
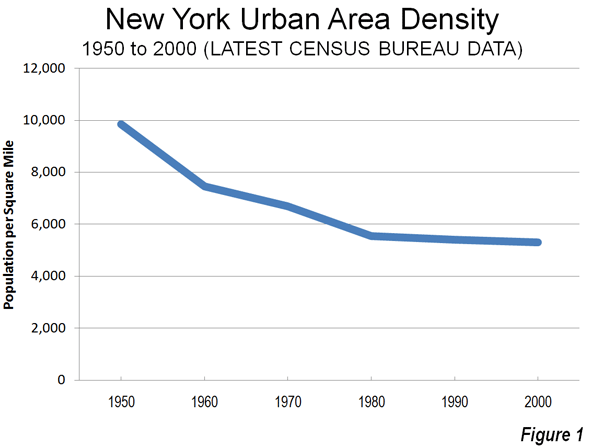
Striking Out on Density: The strikeout results from assumptions that are patently wrong. Cities (urban areas) do not get more dense as they add population. They actually become less dense. For example, the New York urban area has added 50 percent to its population since 1950, yet its population density has dropped by 45 percent (Figure 1). Between 2000 and 2010, most metropolitan population growth, whether in San Francisco, New York, Phoenix, Portland or Houston, was in the lower density suburbs (see: http://www.city-journal.org/2011/eon0406jkwc.html ). The same dispersion is occurring virtually around the world (see: http://www.demographia.com/db-evolveix.htm), from Seoul, to Shanghai, Manila and Mumbai. Rapid urban growth would mean even further dispersion and lower densities, not the higher density neighborhoods Avent imagines. Nonetheless, allowing the more affordable detached housing that people prefer would likely lead to stronger economic growth and more affluent residents in the San Francisco and other over-regulated metropolitan areas.
A "Yes, But" on Productivity: Any comparison of incomes between metropolitan areas needs to take into consideration the cost of living. For example, the San Francisco Bay Area (San Francisco/San Jose) is one of the most expensive places to live in the country. The median house price is more than 2.5 times that of Phoenix, after accounting for income differentials. Avent does not control for the difference in the cost of living, which is largely driven by the higher cost of housing. The lower cost of living neutralizes much of the impact of lower incomes (such as in Houston) in metropolitan areas like Houston, Dallas-Fort Worth, Indianapolis, etc., where the OPEC model has not been applied to land use regulation.
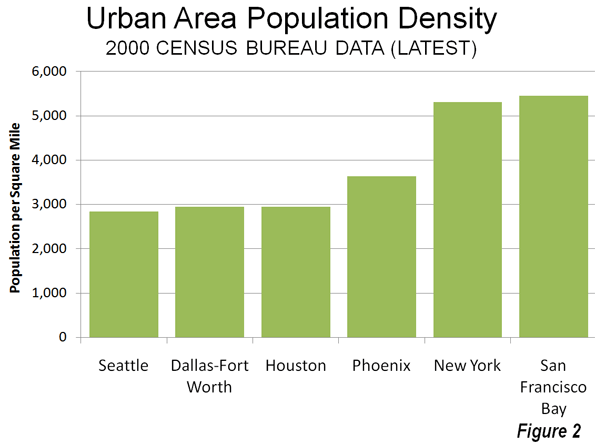
Finally, even controlling for the cost of living, there are substantial exceptions to any density-productivity thesis. For example, some of the greatest productivity gains information technology have come out of the Seattle area, which is the least dense major urban area in the 13 Western states, less dense than Houston, Dallas-Fort Worth and Phoenix. Even more impressively, Seattle's urban density is barely one-half that of New York or San Francisco (Figure 2), yet its gross domestic product per capita is higher than New York and within 2 percent of San Francisco/San Jose. Seattle's substantial contribution to the nation's productivity has occurred while its population density was declining nearly 15 percent (since 1980).
Avent, like many analysts before appears to presume that population growth means higher densities. In fact, urban areas grow by dispersing, not densifying.
The Economist magazine has called on the British government to cancel plans for the HS-2 high-speed rail line that would run from London to Birmingham and Manchester. The Economist said:
...these days politicians across the developed world hope new rapid trains, which barrel along at over 250mph (400kph), can do the same. But high-speed rail rarely delivers the widespread economic benefits its boosters predict. The British government—the latest to be beguiled by this vision of modernity—should think again
The government claims the line will cost £32 billion line, however the international experiences suggests a figure more on the order of £32 and the experience in this corridor itself suggests costs could rise even more (see The High Speed Rail Battle of Britain).
A principal purpose for the line is to bridge the economic gap between the economic dynamo of Southeast England (including London) and the Midlands and North of the country. This does not convince The Economist:
China suspended new projects after a fatal collision of two high-speed trains in July; Brazil delayed plans for a rapid Rio de Janeiro-São Paulo link, after lack of interest from construction firms. Yet governments remain susceptible to the idea that such projects can help to diminish regional inequalities and promote growth.
The Economist doubts this will happen:
In fact, in most developed economies high-speed railways fail to bridge regional divides and sometimes exacerbate them. Better connections strengthen the advantages of a rich city at the network’s hub: firms in wealthy regions can reach a bigger area, harming the prospects of poorer places. Even in Japan, home to the most commercially successful line, Tokyo continues to grow faster than Osaka. New Spanish rail lines have swelled Madrid’s business population to Seville’s loss. The trend in France has been for headquarters to move up the line to Paris and for fewer overnight stays elsewhere.
The Economist reminds the government that:
Britain still has time to ditch this grand infrastructure project—and should. Other countries should also reconsider plans to expand or introduce such lines. A good infrastructure scheme has a long life. But a bad one can derail both the public finances and a country’s development ambitions.
Finally, The Economist says that there is better use for the money.
The £32 billion at its disposal might well yield a higher return if it were spent on less glitzy schemes, such as road improvements and intra-city transport initiatives. If the aim is to regenerate “the north”, the current plan might prove a high-speed route in the wrong direction.
The fully interactive map below indicates job growth and decline for all US counties from 2006 to 2011. These show up as hot or cold spots; red for growth, blue for decline. You can select a state to zoom in on and find a county that way, or simply click on a county to drill in. Once you’ve chosen a county, the table under the map will show you job numbers by industry category.
The data for this graphic comes from EMSI’s Complete 2011.3 dataset, based on data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics and many other sources. Many thanks to Tableau for putting this together. If you have questions or comments about the graphic or the data behind it, please email EMSI's Josh Stevenson.
|
















