
In his new book, The Coming Jobs War, Gallup CEO James Clifton defines what he calls an “all-out global war for good jobs.” Clifton envisions a world-wide struggle for new, steady employment, with the looming threat of “suffering, instability, chaos and eventually revolution” for those who fail to secure new economic opportunities.
In the U.S., this conflict can be seen as a kind of new war battle the states, each fighting not only for employment but for jobs that pay enough to support a middle-class lifestyle.
My colleagues at Praxis Strategy Group and I have looked over data for the period after the economy started to weaken in 2006. Using stats from EMSI, based on data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, we compared sectors by growth, and then by average salary.
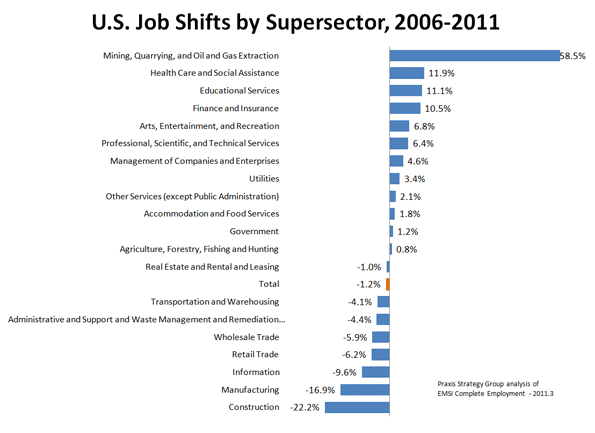
Not surprisingly “recession-proof” fields such as health care and education expanded some 11% over the past five years. More inexplicably, given its role in detonating the Great Recession, the financial sector expanded some 10%.
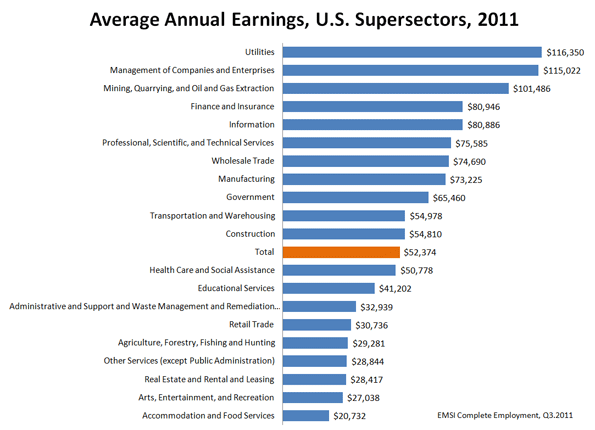
But the biggest growth by far has taken place in the mining, oil and natural gas industries, where jobs expanded by 60%, creating a total of 500,000 new jobs. While that number is not as large as those generated by health care or education, the quality of these jobs are far higher. The average job in conventional energy pays about $100,000 annually — about $20,000 more than finance or professional services pay. The wages are more than twice as high as those in either health or education.
Nor is this expansion showing signs of slowing down. Contrary to expectations pushed by “peak oil” enthusiasts, overall U.S. oil production has grown by 10% since 2008; the import share of U.S. oil consumption has dropped to 47% from 60% in 2005. Over the next year, according to one recent industry-funded study, oil and gas could create an additional 1.5 million new jobs.
This, of course, violates the widespread notion that the future lies exclusively in the information and technology industries. While technology may well be ubiquitous, as a sector it is far from a reliable creator of high-wage jobs. Since 2006 the information sector has hemorrhaged over 330,000 jobs. And those who do have jobs make on average about $20,000 less than their oil-stained counterparts per year.
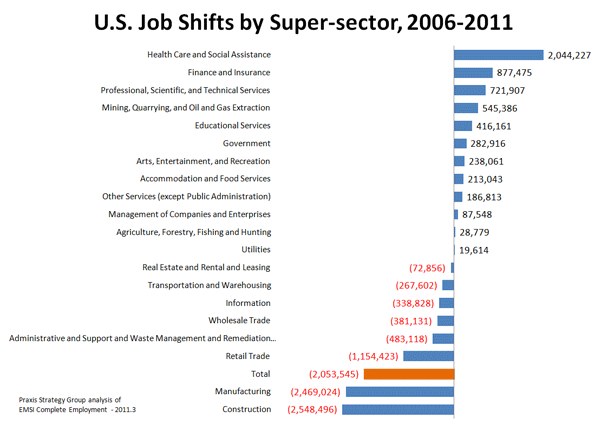
How about those “green jobs” so widely touted as the way to recover the lost blue-collar positions from the recession? Since 2006, the critical waste management and remediation sector — a critical portion of the “green” economy — actually lost over 480,000 jobs, 4% of its total employment. Pay here is lower still, averaging something like $32,000 annually, about one-third that of the conventional energy sector.
The future of the rest of the “green” sector seems dimmer than widely anticipated. One big problem lies in cost per kilowatt, where wind is roughly twice as expensive and solar at least three times as expensive as electricity produced with natural gas. Given the Solydra bankruptcy and their inevitable impact on the renewables industry, it’s also pretty certain that the U.S., at least in the near term, will not be powered by windmills and solar panels.
So instead of tilting windmills or taking out the trash, what about joining the much ballyhooed “creative class”? Not so great a bet for those limited in talent or nepotism. The arts, entertainment and recreation sector gained about half as many total jobs as energy, and the pay is nothing to write home about. The average salary for these creative souls is about $27,000, slightly higher than for food service workers, but barely a quarter of the average salary for the oil and gas-dominated sector.
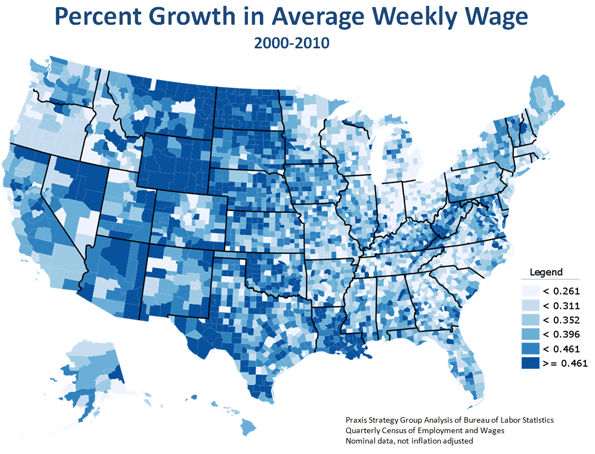
The relative strength of the energy sector can be seen in changes in income by region over the past decade. For the most part, the largest gains have been heavily concentrated in the energy belt between the Dakotas and the Gulf of Mexico. Energy-oriented metropolitan economies such as Houston, Dallas, Bismarck and Oklahoma City have also fared relatively well. In energy-rich North Dakota there’s actually a huge labor shortage, reaching over 17,000 — one likely to get worse if production expands, as now proposed, from 6000 to over 30,000 wells over the next decade.
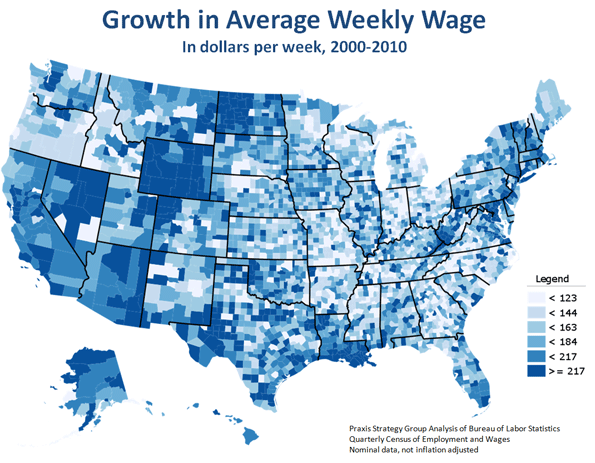
What message does this send to politicians seeking to turn around our moribund economy? Perhaps they should target oil and gas development as a spur not only to new employment, but to the kind of “good jobs” that Gallup’s Clifton speaks about. With the proper environmental controls, these industries could provide a major jolt to the economy while cutting down on energy imports, reducing debts and bringing jobs back home. As long as Americans consume oil and gas, why not produce close to the market and with reasonable environmental controls?
The monthly proliferation of new energy finds can provide a much brighter future than many have anticipated. Industry experts say that the shift in energy exploration is moving from the Middle East to the Americas, with rich deposits of oil and gas uncovered from Brazil to the Canadian oil sands.
Much of the new action is on the U.S. mainland, including the Dakotas, Montana and Wyoming. Increasingly, there’s excitement about finds in long-challenged sections of the Midwest such as Ohio. The Utica shale formation, according to an estimate by Chesapeake Energy, could be worth roughly a half trillion dollars and be, in the words of CEO Aubrey McClendon, “the biggest to hit Ohio, since maybe the plow.”
Ohio now has over 64,000 wells, with five hundred drilled just year. Recent and potential finds, particularly in the Appalachian basin, could transform the Buckeye State into something of a Midwest Abu Dhabi, creating more than 200,000 jobs over the next decade. The new finds could also help Ohio fund its depleted state coffers without imposing either debilitating budget cuts or economically self defeating new taxes.
The energy boom also has sparked a spate of new factory expansions, including a $650 million new steel mill to make pipes for gas pipelines. Other local firms are gearing up to make up specialized equipment like compressors.
Michigan, another perennially hard hit state, is also looking at new energy finds to turbocharge its gradually recovering industrial sector. While risible former Gov. Jennifer Granholm pushed the notion that Michigan’s recovery lay in “cool cities” and green jobs, the state’s current leaders are focusing on more down-to-earth — and under-the-earth — solutions as part of a strategy to revive industrial production.
Such growth anywhere is good news, particularly in Midwestern blue-collar towns that have borne the brunt of the recession. Since 2006 manufacturing and construction have shed some 5 million jobs combined — jobs that pay above-average wages, far better than those earned in growing fields such as health care, education or the lower-end service sector.
The surest road to recovery does not lie in the chimera of “green jobs” or by magically harvesting riches from social networks. It’s in making America a more self-reliant and productive power. The new spate of energy in the Midwest and elsewhere in the country may be one way to do this, if we have the will to take full advantage.
This piece originally appeared at Forbes.com.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and is a distinguished presidential fellow in urban futures at Chapman University, and an adjunct fellow of the Legatum Institute in London. He is author of The City: A Global History. His newest book is The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050, released in February, 2010.
Analysis and charts by Mark Schill, Praxis Strategy Group.
Photo by flickr user thorinside












