NewGeography.com blogs
Chicago's urban core has boomed in a way that makes most other cities jealous. Every time you turn around, it seems, another gem is added to it. The Renzo Piano designed Modern Wing at the Art Institute recently opened its doors to general, if not universal, acclaim, for example.
But while this boom is to be celebrated, and clearly it has been necessary to sustain the animating life force of the city as a whole, there are long term threats that need to be considered.
The first is that all booms tend to contain within themselves the seeds of their own collapse. We've seen that with the dot.com bubble, the real estate bubble, and the finance bubble, the last two of which are really weighing on Chicago. Growth feeds on itself in a type of positive reinforcement loop. If it hits a certain point, it can really take off, as in a typically "hockey stick" diagram. The problem is that some point the trend reaches the point of exhaustion, and the hangover can be a bear. Most stable systems employ negative feedback controls or stabilizers to "take away the punch bowl just as the party is getting started".
The real challenge, however, is what Jane Jacobs called the "self destruction of diversity". Thriving urban districts require a mixtures of users and uses acting to mutually sustain and energize a neighborhood. But what has a tendency to happen is that, as an area becomes popular, land values go up and rents go up. There is greater demand for and competition for the space. Because of this, the most economically successful use of the moment tends to become increasingly dominant. This is particularly the case if that use benefits from face to face interactions among multiple players in the space and clustering economics.
Jacobs also talked about the requirement that neighborhoods contain buildings of a mixture of ages, such that they require differing levels of economic rent. New enterprises, particularly in wholly new fields, often require space that is available at low cost. So if there are no low cost buildings in an area, tomorrow's new industries can't often get started in a place at all. While she didn't quite put it this way, this notion is often paraphrased as "new ideas require old buildings".
The boom in Chicago causes concern on both of these fronts. Firstly, the great Loop area is increasingly dominated by two uses: financial and business services for the global city function of Chicago, and entertainment/tourism. To some extent, the Loop has always had these characteristics as a typical CBD. And in many respects, the streets are far more active today than they were in an era not that long ago when the streets in the Loop really did roll up at 6pm.
The real problem is that the boom in the Loop has generated enormous opportunity for profit in the redevelopment of older buildings. Many older buildings have been demolished completely, or preserved only the form of the "facadectomy". A number of vintage office skyscrapers have been converted to residential use. The high rent district, which used to apply mostly to the core of Loop, now extends far to the West and South instead of just the traditional north. The number of places where one can obtain low-rent space in the greater Loop area would appear to have declined significantly.
The same forces are operating in residential areas, which are increasingly taking on the cast of New Urbanist suburbs. Housing prices keep out all but the already affluent in many places. Rents have followed suit, leading to a predominance of swanky establishements catering primarily to consumption by the upscale: restaurants, clubs, boutiques, spas, etc. A number of formerly industrial districts have been reborn as more or less single use large format retail strips.
What will the long term affect of this be? I don't know. I do think it is something worth of consideration. Affordable housing is obviously something that is on the radar of many groups. But the idea of affordable office or industrial space less so. We want the Loop to be successful, but also I think there should be policies developed that are designed to actively sustain its diversity over time.
The danger is that the Loop becomes increasingly concentrated in ever most high value specialized services. (I've even suggested how we might encourage this through cross-regional collaboration). This can be good in that it keeps Chicago a player at the pinnacle of the global economy. But it also exposes Chicago to the risk of niche exhaustion. And with the global city functions an artifact of globalization as we know it today, any disruption or further evolution of that model could seriously hit Chicago.
As I've long argued, in an ever more rapidly changing, uncertain world, it is critical for cities to have a diversity of strategies and future options for success, and not put all their eggs in one basket. Chicago needs to continue reinforcing its success, but it also needs to look at how to diversify that success so that when, as it inevitably will, economic needs change, Chicago is right there with the next new thing. While picking winners and losers is a problematic concept, at a minimum the city should be looking at how to preserve the conditions necessary for success.
Interestingly, the city has already taken some steps here. It created the concept of a "Planned Manufacturing District" to prevent residential encroachment into surviving manufacturing zones like the Kinzie Corridor. A good move. While mono-use isn't always a good thing, for a traditionally manufacturing area, I think this is a decent strategy. We should be looking at similar means of preserving the favorable economics for new ideas in the urban core as well.
More Chicago:
Chicago: A Declaration of Independence
Reconnecting the Hinterland Series
Part 1A: Metropolitan Connections
Part 1B: High Speed Rail
Part 2A: Onshore Outsourcing
Part 2B: On Innovation
On the Chicago Economy
Chicago: Corporate Headquarters and the Global City
The Financial Crisis: Good for Chicago?
The battle to find ways to close California's gaping $24 billion budget shortfall continues, with Governor Schwarzenegger calling for deep cuts and reorganization throughout state government. Last week, making a "rare speech to a joint session of the Legislature," Gov. Schwarzenegger argued that the state has "run out of time," and faces a situation where "Our wallet is empty, our bank is closed, and our credit is dried up".
The challenges facing California's policy makers in balancing the budget can be examined by checking out the Los Angeles Times' "Interactive California Budget Balancer". While the state has many different options available to it, making cuts to potentially popular programs will only serve to irritate interest groups which argue for the efficacy and essential nature of their favored programs. Couple this reluctance to make cuts with popular resistance to tax increases, recently seen when voters rejected a set of measures on May 19, and one can better understand the true magnitude of the budget impasse facing the state.
“A new business model” is what Jack Nerad of Kelly Blue Book called the proposed sale of Saturn by General Motors (GM) to Roger Penske’s Penske Automotive Group.
What makes it a new model is that Penske would only buy the brand and the dealer network. Penske would subcontract vehicle production other manufacturers, though for the first two years, the GM Saturn plant would produce the cars. Doubtless, Penske will buy vehicles from assembly plants able to provide the best quality for the dollar, establishing competition at the factory rather than corporate level. This radical departure solves the fundamental problem leading to the near-death of the American automobile industry.
Following World War II, America had little competition. Industrial powers such as in Europe and Japan were flat on their backs and American manufacturers had a “clear field.” American labor and management bid up the price of heavy manufactured goods so much that they became less competitive when war torn economies recovered.
Americans paid over and over again in their automotive purchases. They paid first through reliability difficulties that were the inevitable result of attempting to compete on price with foreign firms with costs that were competitive in world markets. Finally, they paid with more than $60 billion in loans to General Motors, GMAC and Chrysler. Canadians also paid twice, most recently in more than $13 billion in loans that make their per capita contribution substantially higher than that of Americans. It is not at all clear that North American taxpayers will ever see these amounts repaid (American taxpayers are still waiting for the first penny of repayment from Amtrak on loans made more than 25 years ago).
The recent loans were the result of a political consensus that GM and Chrysler were “too big to fail.” In an industry characterized by the Penske-Saturn model, the too-big-to-fail problem would be removed.
There was terrible news for Dayton this week as the city's last Fortune 500 company, NCR, founded locally in 1884, announced it was moving its headquarters to Atlanta. The Dayton Daily News is the place for complete coverage.
This is bad news not just for Dayton, but for the state of Ohio and the entire Midwest. Firstly, it illustrates the plight of the smaller cities of the Midwest, the ones below one million in metro area population that I usually don't write much about. These cities, including places like Dayton, Youngstown, and Toledo, are often struggling. Unless they are a state capital and/or home to a major state university, they just don't seem to have quite the scale necessary to operate in the globalized economy. These cities have special challenges and I won't profess to have answers for them.
Secondly, this is further damage to the economic reputation of the Midwest as a whole. Loyal readers know that I've been skeptical of cross-regional collaboration as a panacea (though I've also written some positive things about it). However, there are clearly issues that affect the Midwest as a whole. It has, for example, a collective reputation as the Rust Belt that probably only Chicago is able to overcome.
This reputation creates formidable brand headwinds in trying to attract the talent needed to compete in the 21st century. The Atlanta Business Chronicle had an interesting take on the NCR move, with one anonymous source attributing it to talent issues with Dayton. "They [NCR] can’t recruit talent to move to Dayton, Ohio."
So what, you might say. It's Dayton. But my town is way cooler than Dayton. Well, the problem extends well beyond Dayton. Consider Ann Arbor. If any city in the Midwest can claim to be a winner in a the knowledge economy, it has to be the home of U of M, the best public university in the Midwest. But according to an article in the Journal, "Despite Ann Arbor's educated work force, employers here find Michigan's reputation as a failing manufacturing economy can deter potential hires from moving to the state."
In short, this thing affects everybody. Even the best regional performers will be fighting horrible brand headwinds as long as the region in which they are embedded continues to fail. It's like a larger version of what I've long said about the Hoosier State, that there can't be a long term prosperous Indianapolis without a prosperous Indiana.
The lessons of Dayton and NCR are not being lost on people locally and around the state at least. Local blog Dayton Most Metro asks, "Are we ready to wake up yet?"
And a columnist in the Cleveland Plain Dealer chimes in with a call to arms for his city.
When Ohio cities lose storied corporate birthrights to the likes of Beijing, Calcutta, or even the green fields of Ohio suburbia, I understand potentially insurmountable market forces at work.
But when we continue to lose to the likes of Georgia, I only recognize underperforming leadership and a criminal failure to anticipate market realities.
In trying to understand the meaning of it all, we should reflect on the somber and lonely sentiments of a Dayton Daily News editorial that noted Wednesday that the city is now on its own.
Closer to home, Cuyahoga County continues to inch closer to its civic funeral. Not only do we continue to bleed off population and shutter what is left of our industrial base, we continue to act in a predictable political fashion that hastens our day of reckoning.
The inability of Cuyahoga County officials to agree on government reform tells the world that Northeast Ohio continues to be no place to do business. Like Dayton, our region remains a corporate cherry-picker's fantasy.
Soon there will be nothing left to govern in Cuyahoga County.
This post originally appeared at The Urbanophile.
Would you like to avoid recessions altogether?
You can come close if you live in the right place.
This report looks at the period January 1991 through April 2009 – a period of 220 months that includes three recessions. Since employment rises and falls monthly because of seasonal trends (school year, holiday retail and more), this report uses 12-month employment growth rates as the measurement criteria – the employment in a given month compared to the employment 12 months earlier. This eliminates seasonality and allows us to compare, if you will, apples with apples.
The metric in this analysis is the percent of months where the 12-month employment growth rate is positive.
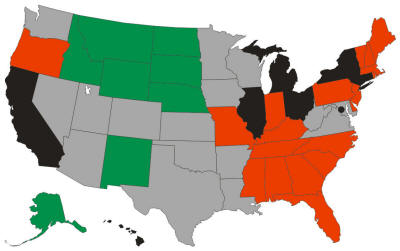 Using employment growth rates as the measurement criteria: Using employment growth rates as the measurement criteria:
Alaska is 99.1% recession-proof since employment was growing for 218 months out of 220.
Michigan is 51.8% recession-proof since employment was growing for 114 months out of 220.
All the states are shown in the graphic, color-coded as follows:
- Green is 90% or more
- Grey is 80% to 90%
- Red is 70% to 80%
- Black is less than 70%
Some metropolitan areas are also relatively recession-proof:
| Area |
Share of months where 12-month job growth rate is positive
|
| Grand Junction, CO |
100.00%
|
| McAllen-Edinburg-Mission, TX |
99.50%
|
| Olympia, WA |
99.10%
|
| Bismarck, ND |
98.60%
|
| Anchorage, AK |
97.70%
|
| Fargo, ND-MN |
97.70%
|
| Tyler, TX |
97.30%
|
| Greeley, CO |
96.80%
|
| Iowa City, IA |
96.40%
|
| Sioux Falls, SD |
96.40%
|
| Cheyenne, WY |
95.90%
|
| Columbia, MO |
95.90%
|
| Coeur d'Alene, ID |
95.50%
|
| College Station-Bryan, TX |
95.50%
|
| Billings, MT |
95.00%
|
| Fayetteville-Springdale-Rogers, AR-MO |
94.50%
|
| Laredo, TX |
94.50%
|
| Las Cruces, NM |
94.50%
|
| Valdosta, GA |
94.50%
|
| Killeen-Temple-Fort Hood, TX |
94.10%
|
| Rapid City, SD |
94.10%
|
| Bellingham, WA |
93.60%
|
| Ogden-Clearfield, UT |
93.60%
|
| Knoxville, TN |
93.20%
|
| St. George, UT |
93.20%
|
And, unfortunately, some metropolitan areas are not very recession proof:
| Area |
Share of months where 12-month job growth rate is positive
|
| Baltimore City, MD |
17.70%
|
| Flint, MI |
28.60%
|
| Detroit-Livonia-Dearborn, MI Metro |
34.10%
|
| Philadelphia City, PA |
35.50%
|
| Dayton, OH |
37.30%
|
| Mansfield, OH |
38.20%
|
| Youngstown-Warren-Boardman, OH-PA |
41.80%
|
| Muncie, IN |
42.70%
|
| Kingston, NY |
43.60%
|
| Waterbury, CT NECTA |
45.50%
|
| Binghamton, NY |
47.30%
|
| Lima, OH |
47.30%
|
| Springfield, OH |
48.20%
|
| Detroit-Warren-Livonia, MI |
49.10%
|
| Lansing-East Lansing, MI |
50.00%
|
| Saginaw-Saginaw Township North, MI |
50.50%
|
| Ann Arbor, MI |
51.40%
|
| Cleveland-Elyria-Mentor, OH |
52.70%
|
| Decatur, IL |
52.70%
|
| Terre Haute, IN |
53.60%
|
| Canton-Massillon, OH |
54.10%
|
| Battle Creek, MI |
54.50%
|
| Jackson, MI |
55.00%
|
| Niles-Benton Harbor, MI |
55.00%
|
You can’t necessarily judge a metropolitan area by its State’s employment growth rates. For example, Georgia is only 73.6% recession-proof yet Valdosta is 94.5%. Indiana is 74.5% yet Indianapolis is 90.0%. Missouri is 72.3% yet Columbia is 95.9%.
A complete list of states and metropolitan areas is available at http://jobbait.com/a/rpa.htm.
The data in this report present only part of a recession-proof picture of states and metropolitan areas. Think of them as a long-term picture from 1990 through April 2009. They do not necessarily represent what’s happening today. For example, Olympia WA which is the second-most recession-proof metropolitan area long term has declines in the last two months, March and April 2009. And, this will change next month and the month after.
This report was written by Mark Hovind, President of JobBait. Mark helps six and seven figure executives find jobs by going directly to the decision-makers most likely to hire them. Mark can be reached through www.JobBait.com or by email at Mark@JobBait.com.
|
 Using employment growth rates as the measurement criteria:
Using employment growth rates as the measurement criteria:











