
Everywhere you look – from the White House to Wall Street – they are painting a sunny picture of recovery, free from any gloomy ideas. Bernie Madoff is in jail, Goldman Sachs is repaying their bailout money, and everywhere they look they see “green shoots.”
Yet according to the Congressional Budget Office (CBO), the US economy and federal government are headed for doom. We are on a completely unsustainable path economically and financially. The CBO updated their forecasts after our June piece on the State of the Economy. In their updated Budget and Economic Outlook, CBO clearly concludes that the current rate of high spending and low revenues has the nation on an unsustainable fiscal course. Unemployment won’t drop below 5% until 2014. As a result, according to the latest country risk rankings by Euromoney magazine [http://www.euromoney.com, subscription required for full access] Canada, Australia and most of Scandinavia have passed the US as safer places to invest in business.
These predictions of doom are, in fact, based on the best-case scenario of 3 percent economic growth next year and 4 percent the year after that; plus the expiration of tax cuts and no new stimulus or bailout packages. Whether we call it a Panic, a Depression, a Recession or a Downturn, it all means the same thing. The nomenclature has been softened over the decades to remove that ever so gloomy feeling folks get when things are bad. If you still have a job, you know someone who has been laid off, had their hours cut, etc. I just received my first new piece of business since February. Things are tough everywhere you look.
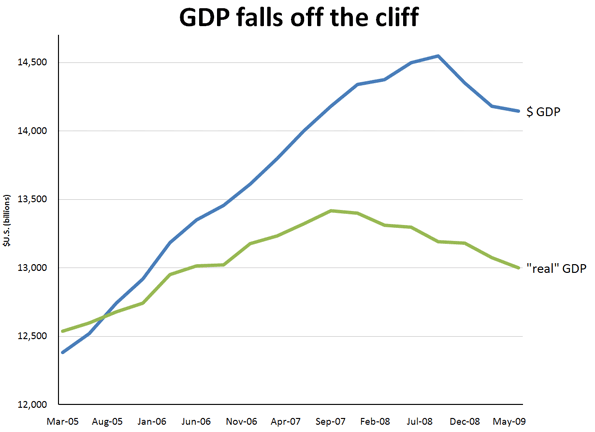
GDP this year ($14,143 billion) is about where it was two years ago in actual dollar terms ($14,180 billion, third-quarter 2007). Accounting for inflation in consumer prices, our economy is closer to the level it was at the end of March 2006 or even back to the end of 2005. Actual dollar GDP peaked in September 2008 but I prefer the regular “real” GDP, adjusted for changes in what a dollar will buy you, which peaked in the third quarter of 2007 – we live in the real world, using real dollars to pay for real things.
The importance of changes in the real-dollar economy become most obvious when we consider international trade, which has been on the minds of the leaders of the G-20 nations in Pittsburgh this week. The fact that US consumers sustained and even increased their demand for imported goods until the onset of the global recession and in the face of a declining dollar lends credence to President Obama‘s plan to discuss what the world, not just what the US, can do to “lay the groundwork for balanced and sustainable economic growth.”
On the one hand, our consumption of imported goods contributed to ours and the world’s economic growth. This fuels concern over whether or not the US can keep the promise to not impose new trade barriers before the end of 2010 and the world’s willingness to continue to buy our debt in the form of US Treasury bonds. At the same time, as Kansas City Federal Reserve Bank President Thomas Hoenig said last week in a speech I attended in Omaha, we need the world’s consumers to continue buying US goods in order to maintain our position as the “industrial leader of the world.” It’s a delicate balance, at best.
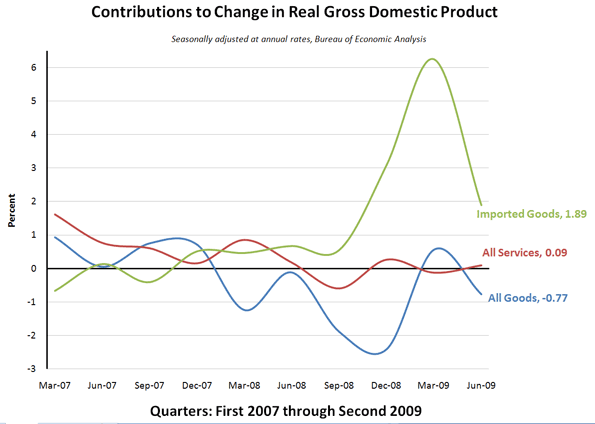
The late 2007 nose dive in the “real” economy exposed the trouble brewing on the housing front, when we became aware of the explosion in credit derivatives, and when many of us started warning people about the insanity taking place in U.S. bond markets. No matter how you measure it, we would need about a 3 percent increase in GDP by next summer just to get back to where we were the last time everyone felt good about their money.
 Data from Bureau of Economic Analysis; author’s calculations
Data from Bureau of Economic Analysis; author’s calculations
So, why are we hearing such a positive spin on the economic news? One reason is the lack of understanding among reporters – most of them probably studied literature or journalism in college – not finance or economics. New York Times economics reporter Edmund L. Andrews is a perfect example. He just published a book describing “how he signed away his life for a toxic loan to buy a house in Silver Spring that he couldn't really afford.” The Washington Post reviewer called the book “bright and breezy.” No gloom there!
At the same time that he was signing the papers for an outsized mortgage, Andrews was writing articles like this gem from September 1, 2007 – just as the real economy was perched on the edge of the cliff – where he reports on Federal Reserve Bank Chairman Ben Bernanke saying he will “prevent chaos in the mortgage markets from derailing the economy.” The stock market climbed nearly 1 percent that day to close at 13,357.74 – it closed at 9,820.20 last Friday. Yet, Mr. Andrews still has a job with the New York Times – unlike millions of his readers – writing about topics like troubled mortgages.
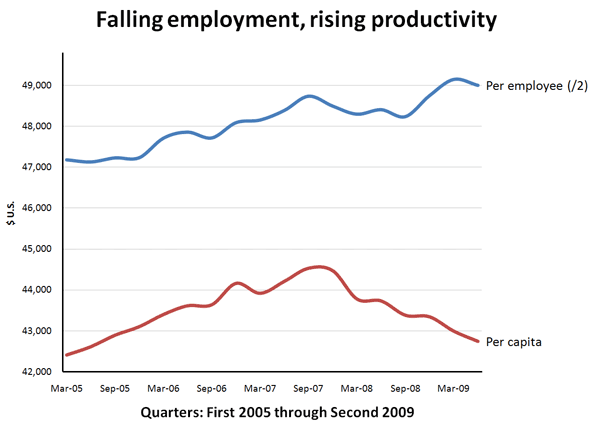 Data from Bureau of Economic Analysis and Census Bureau. Per employee divided by 2 for scale.
Data from Bureau of Economic Analysis and Census Bureau. Per employee divided by 2 for scale.
But what about the recent stock market rise? We should not be surprised if business profits are up: fewer people working means that the output per worker has been increasing since the end of 2008. GDP per capita (per person in the population), on the other hand, has been decreasing since the end of 2007 – an indication of a falling standard of living.
The next few months are a time to focus, concentrate, plan, and follow-through. We are at a turning point comparable to the beginning of the Industrial Revolution and the system of capitalism that financed it. By frantically printing money and creating credit through bank bail-outs, the Federal Reserve and the Treasury are boosting the stock market by pumping in about $150 billion a month into corporate securities, increased auto sales (with government rebates) and home sales (with government first-time buyer tax credits).
The problem is that these three pieces – banking, cars and homes – are not the whole economy, and, since they depend on government debt, none of these “green shoots” are sustainable on their own. Keep your eye on the big picture (the Kiplinger Recovery Index is a handy one-stop) – and don’t relax until all the indicators are green.
Susanne Trimbath, Ph.D. is CEO and Chief Economist of STP Advisory Services. Her training in finance and economics began with editing briefing documents for the Economic Research Department of the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco. She worked in operations at depository trust and clearing corporations in San Francisco and New York, including Depository Trust Company, a subsidiary of DTCC; formerly, she was a Senior Research Economist studying capital markets at the Milken Institute. Her PhD in economics is from New York University. In addition to teaching economics and finance at New York University and University of Southern California (Marshall School of Business), Trimbath is co-author of Beyond Junk Bonds: Expanding High Yield Markets.












