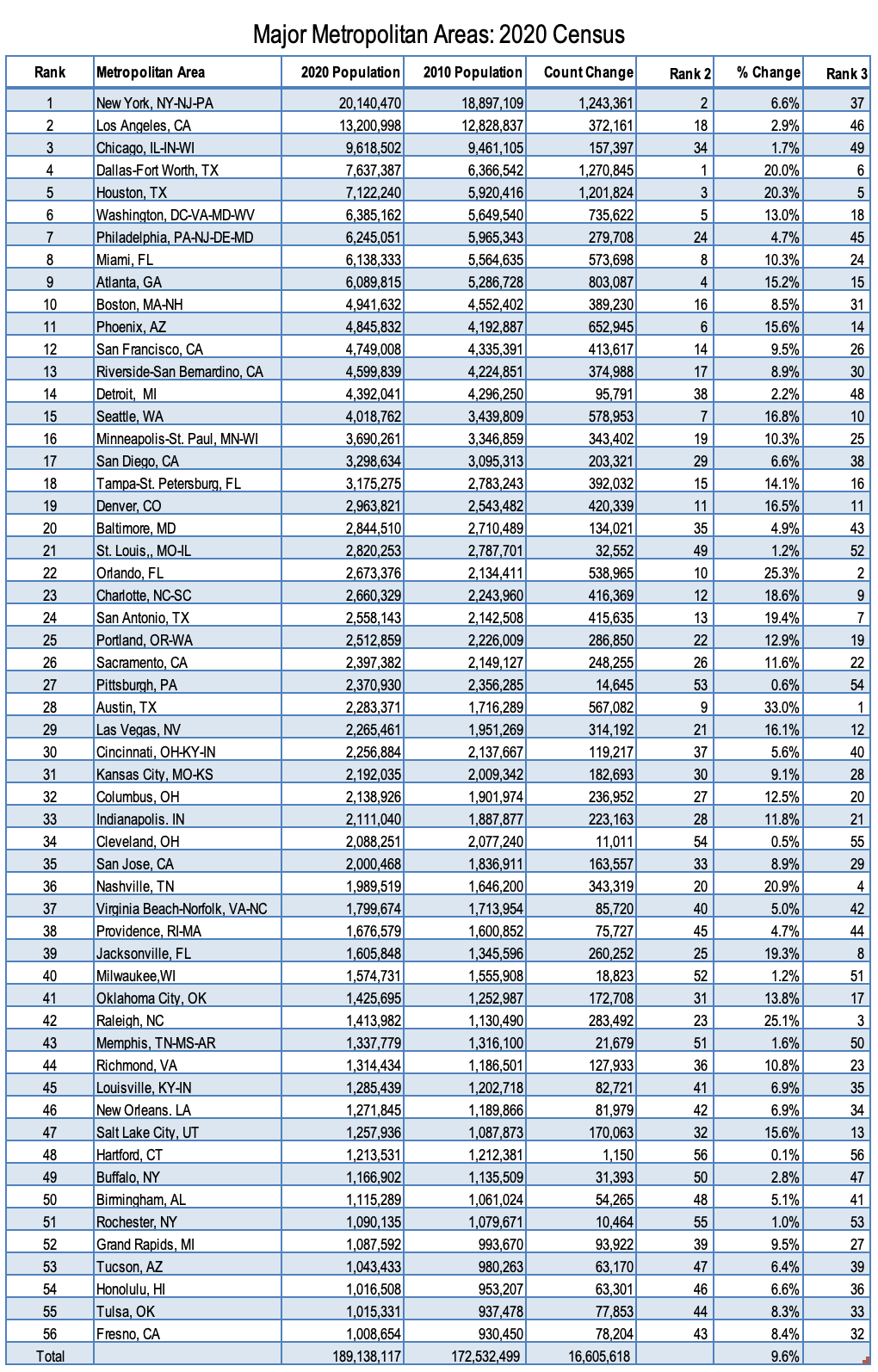
The recently released 2020 Census count indicates that the nation now has 56 major metropolitan areas (over 1,000,000 residents), with the addition of Fresno, Tulsa and Honolulu toward the end of the decade. The Table below provides detailed information.
New York, the largest metropolitan area, climbed to 20.1 million from 18.9 million in 2010. New York had the second largest population increase, at 1,243,000. This was a 6.6% population increase, slightly below the 7.4% national growth rate. For the first time in decades, New York led Los Angeles in population growth, and it wasn’t even close. New York’s population increase was 3.3 times that of second ranked Los Angeles, which gained 372,000. The Los Angeles percentage growth rate (2.9%) was stunningly low for a metro that had been among the faster growing in the world for decades. Out of the 20 largest metropolitan areas, Los Angeles grew slower than all but two. Los Angeles edged up to 13.2 million according to the census count.
Chicago ranked third, at 9.6 million, having added only 157,000 (1.7%) over the last 10 years.
Fourth ranked Dallas-Fort Worth reached 7.6 million, an increase of 1,271,000, the largest increase of any metropolitan area (20.0%). However, in-state rival Houston had greater percentage growth, at 20.3%, adding 1,202,000 to reach 7.1 million and now ranks 5th largest.
Washington continued its strong growth, adding 736,000 new residents, the fifth strongest gain (13.0%). Washington now ranks sixth largest in the nation, at 6.4 million. During the decade, Washington passed Philadelphia, now ranked 7th , having also been passed by Houston and by Dallas-Fort Worth in the 2000s. In the 2020 census and since the 1960 census, Philadelphia had been the nation’s fourth largest metropolitan area. Philadelphia added 278,000 residents, with a population of 6.2 million in 2020.
Boston added 389,000 residents (8.5%) since 2010 and ranked 10th. Boston had a population of 4.9 million. Phoenix ranked 11th and had a 653,000 population increase (15.6%). San Francisco reached 4.8 million, with Riverside-San Bernardino following closely at 4.7 million. Both of these California metros had larger census count increases than Los Angeles.
Fourteenth ranked Detroit grew by nearly 100,000, for a 2.2% increase, which is rivals that of Los Angeles. Detroit’s count was 4.4 million. Detroit was passed by Phoenix and Riverside-San Bernardino over the decade.
Seattle ranked 14th and had a population of 4.0 million. Seattle gained 579,000 residents for a growth rate of 16.8%.
The fastest growing major metropolitan area was Austin, at 33.0% (567,000). Austin reached 2.3 million and ranks 28th largest. One other major metropolitan area had growth over half-a-million, Orlando, at 539,000, a growth rate of 25.3%. Orlando had a count of 2.7 million, ranking 22nd.
Overall, the major metropolitan areas grew above the national rate, at 9.4%. The 2020 total count for the 56 metros was 189.1 million, representing 57.1% of the national population. This is up from 55.9% in 2010. None of the major metros lost population, though there were some very thin gains. The slowest growing was Hartford, at 0.1%, followed by Cleveland (0.5%) and Pittsburgh (0.6%). Finally, areas outside the historical core municipalities had 78.2 % of the population growth, somewhat more than their 73.4% 2010 share of major metro population (see Note below).
Click the image above to download a PDF of the census information (opens in new tab or window)
Note: This definition of “suburbs” excludes functionally suburban areas within historical core municipalities. About 58% of historical core municipality population is functionally suburban or exurban, according to the City Sector Model, while 86% of the major metro population is functionally suburban or exurban.
Wendell Cox is principal of Demographia, an international public policy firm located in the St. Louis metropolitan area. He is a founding senior fellow at the Urban Reform Institute, Houston, a Senior Fellow with the Frontier Centre for Public Policy in Winnipeg and a member of the Advisory Board of the Center for Demographics and Policy at Chapman University in Orange, California. He has served as a visiting professor at the Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers in Paris. His principal interests are economics, poverty alleviation, demographics, urban policy and transport. He is co-author of the annual Demographia International Housing Affordability Survey and author of Demographia World Urban Areas.
Mayor Tom Bradley appointed him to three terms on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission (1977-1985) and Speaker of the House Newt Gingrich appointed him to the Amtrak Reform Council, to complete the unexpired term of New Jersey Governor Christine Todd Whitman (1999-2002). He is author of War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life and Toward More Prosperous Cities: A Framing Essay on Urban Areas, Transport, Planning and the Dimensions of Sustainability.













